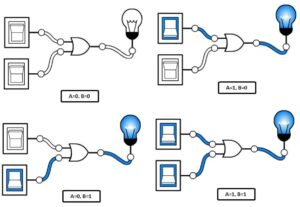
Introduction
Are you curious about the tiny chips that power our everyday devices? Have you ever wondered how complex circuits are integrated onto a single piece of silicon? Welcome to the fascinating world of VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration) design, where engineers work their magic to create the heart and soul of modern electronics. In this beginner-friendly guide, we’ll unravel the mysteries of VLSI design, differentiate between digital, analog, and mixed-signal systems, and help you understand them using simple analogies.
Follow us on LinkedIn for everything around Semiconductors & AI
What is VLSI Design?
VLSI design is like building a miniature city on a silicon chip. Imagine a city with countless buildings, roads, and intricate systems, all packed within a limited space. VLSI designers create these tiny cities, known as integrated circuits (ICs), on a silicon wafer using advanced techniques. These ICs are the brains behind everything from smartphones and laptops to smart appliances and cars.
Read more: What the hell is ASIC design ?
Digital vs. Analog vs. Mixed-Signal: The Basics
Think of digital, analog, and mixed-signal systems as different languages that chips use to communicate.
Digital Systems: These are like light switches – they have two states: on and off. In VLSI design, digital systems process and store information as sequences of 0s and 1s. They are great for performing tasks that involve logic and calculations, like arithmetic operations or decision-making processes.
Analog Systems: Analog systems are like dimmer switches that provide a range of values. Unlike digital systems, which work with discrete states, analog systems work with continuous signals. They’re used to process real-world phenomena like sound, light, and temperature, which can have infinite variations.
Mixed-Signal Systems: Mixed-signal systems are like a bilingual person who can speak both digital and analog languages. They combine the strengths of digital and analog systems to handle tasks that involve both discrete and continuous signals. These systems are commonly found in applications like data conversion (e.g., converting analog audio into digital data for your music player).
Analogies to Simplify the Concepts
Digital System Analogy: Traffic Lights
Imagine a set of traffic lights controlling the flow of cars at an intersection. The lights have two states – green (on) and red (off). Just as the traffic lights manage the movement of vehicles, digital systems process data by flipping between 0s and 1s, managing the flow of information.
Analog System Analogy: Thermostat
Picture a thermostat in your home that controls the temperature. As the temperature changes, the thermostat adjusts the heating or cooling gradually, rather than instantly switching on or off. Similarly, analog systems work with continuous signals, processing real-world changes smoothly.
Mixed-Signal System Analogy: Multilingual Translator
Think of a person who can fluently translate between two languages. In the same way, mixed-signal systems can convert information seamlessly between digital and analog domains. They act as bridges, ensuring smooth communication between the discrete world of 0s and 1s and the continuous world of real-world signals.
Conclusion:
In a nutshell, VLSI design is the art of creating intricate microcosms of technology on a silicon canvas. Digital systems process data in binary, like traffic lights managing cars. Analog systems handle continuous signals, similar to thermostats regulating temperature. Mixed-signal systems are the translators, seamlessly converting between digital and analog languages.
Next time you hold a smartphone or use a smart device, you’ll have a deeper appreciation for the incredible work that VLSI designers do to bring these technologies to life.
The tiny chips they create are truly the unsung heroes of the digital age, orchestrating the symphony of modern life. So, the next time you marvel at the wonders of your gadgets, remember the world of VLSI design that makes it all possible.