In the rapidly evolving landscape of computer memory technology, Micron Technology Inc. has made a groundbreaking announcement called NVDRAM. Micron will unveil a groundbreaking paper at the upcoming IEDM, known for highlighting electronic device advancements. The paper introduces a novel memory technology: 32Gbit NVDRAM, a non-volatile ferroelectric memory.
Nirmal Ramaswamy, Micron’s VP of advanced DRAM and emerging memory, authored the paper. It’s titled “NVDRAm: A 32Gbit Dual Layer 3D Stacked Non-Volatile Ferroelectric Memory with Near-DRAM Performance for Demanding AI Workloads,” presenting the world’s first 32Gbit dual-layer ferroelectric memory technology. This marks a significant innovation in memory.
The NVDRAM Technology
NVDRAM combines ferroelectric memory advantages like non-volatility and durability with performance surpassing NAND flash memory. It offers read/write speeds similar to DRAM. This makes NVDRAM ideal for demanding AI workloads and large neural network models.
The architecture features a 5.7nm ferroelectric capacitor for charge retention within a 1T1C DRAM structure. Dual-gated polycrystalline silicon transistors control memory access. Memory layers are stacked, showcasing Micron’s expertise in compact and intricate memory designs, residing above a CMOS access circuit layer on a 48nm pitch.
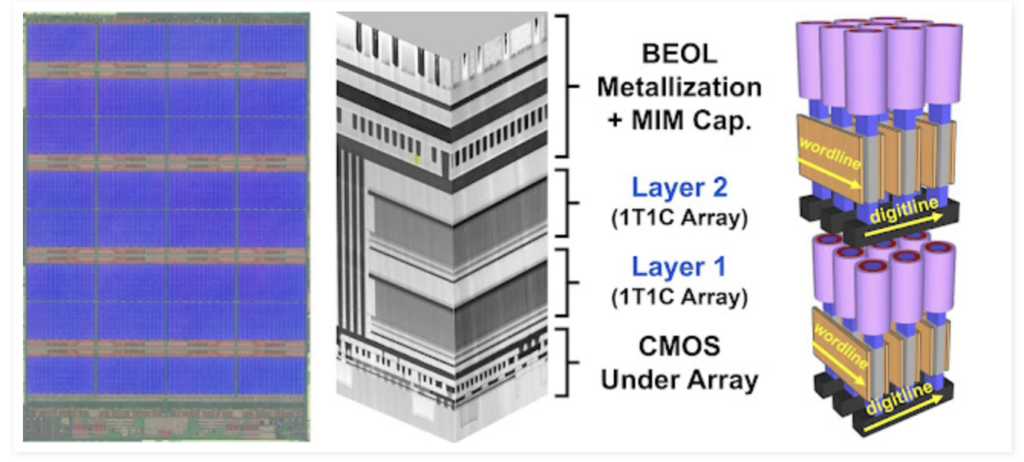
Displayed above are three key visual representations illustrating the 32Gb NVDRAM. The left image showcases the ultimate die layout, while the center image exhibits a scanning electron microscope (SEM) cross-section of the memory, elucidating its 1T1C memory layers fabricated over a CMOS array. On the right side, a schematic diagram elucidates the NVDRAM memory arrays, revealing the polysilicon access device featuring orthogonal wordline (WL) and digitline (DL), alongside the ferroelectric memory cells.(Image Credits: IEDM)
Read More: Why can’t we Scale memory chips?
Claim of Micron NVDRAM Technology
Contemporary research often centers on innovative computer architectures such as near-memory compute and processing-in-memory. However, Micron researchers stress the need to improve existing compute architectures by leveraging more efficient memory solutions right away.
The paper’s summary underscores that this technology represents a groundbreaking achievement, introducing the world to the first-ever dual-layer, high-performance, 32Gbit stackable nonvolatile ferroelectric memory technology. Micron aptly labels this technology as non-volatile dynamic random access memory (NVDRAM), a seemingly contradictory term highlighting its unique characteristics.
Read More: Explained: What the hell is memory?
Advantages and Implications
This breakthrough in memory technology holds immense promise for the industry and computing at large. The merger of ferroelectric memory benefits—non-volatility and durability—with performance surpassing NAND flash memory marks a significant leap forward. NVDRAM boasts faster data movement and superior energy efficiency compared to traditional DRAM, potentially revolutionizing memory solutions for the ever-growing AI landscape.
The implications of NVDRAM extend to improved performance in AI applications, where speed and efficiency are paramount. The potential to stack these memory layers further amplifies its capacity, making it an exciting prospect for future memory demands in AI and other data-intensive applications.
Read More: Who invented memory..Intel or Toshiba?
Future Prospects and Commercialization
While the unveiling of NVDRAM is a remarkable achievement, discussions regarding its commercialization remain speculative. The reception and feedback at IEDM are critical. They will shape the technology’s path to commercial viability. Nonetheless, the innovation showcased by Micron opens a new chapter in memory technology, promising advancements that could reshape the landscape of computing and AI.
In conclusion, Micron’s unveiling of the NVDRAM technology stands as a testament to the relentless pursuit of innovation in the memory industry. As we eagerly await further developments and insights from the IEDM presentation, the future looks promising for memory technologies that can potentially redefine the way we process and store data.
Reference:
[1]. www.ieee-iedm.org