Introduction
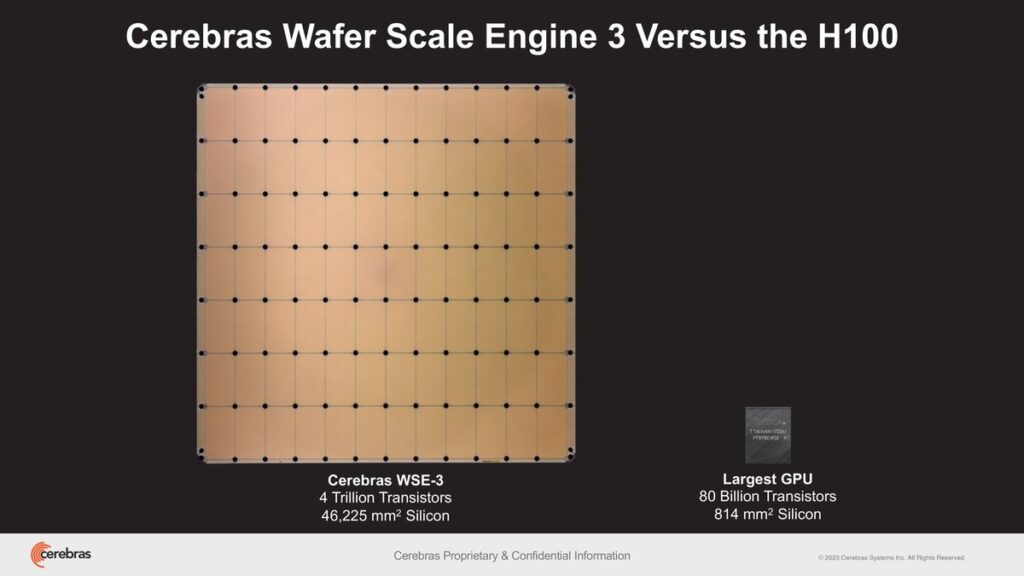
Cerebras Systems has unveiled its Wafer Scale Engine 3 (WSE-3), a breakthrough AI wafer-scale chip with double the performance of its predecessor, the WSE-2. This new device packs 4 trillion transistors made on TSMS’s 5nm-class fabrication process; 900,000 AI cores; 44GB of on-chip SRAM; and has a peak performance of 125 FP16 PetaFLOPS. Ceberas’s WSE-3 will be used to train some of the industry’s largest AI models and has a Wafer scale AI Chip.
Follow us on Linkedin for everything around Semiconductors & AI
Cerebras wafer-scale AI Chip: WSE-3’s Performance Leap
WSE-3 delivers two times the performance of the previous generation, WSE-2, according to Cerebras. The new, superfast chip is built for organizations looking to train large AI models and powers Cerebras’ CS-3 AI supercomputer. In terms of scalability, the CS-3 can be configured in clusters of up to 2048 systems. This scalability allows it to fine-tune 70 billion parameter models in just one day with a four-system setup
With 4 trillion transistors packed into its architecture, the WSE-3 stands as the largest chip available, designed specifically for training expansive AI models, including those with up to 24 trillion parameters.
This is a significant breakthrough, as power consumption has been a major bottleneck in scaling up AI systems. Training a complex AI model in half the time without needing to upgrade your entire infrastructure drastically improves efficiency.
Read more Comparison of NVIDIA’s A100, H100, and H200 for Dominance in High-Performance Computing – techovedas
What are wafer scale chips?
Wafer-scale integration is the idea that you make a single chip out of the whole wafer. You skip the step of cutting the wafer up — with one chip there is nothing to cut.
Typically containing billions of transistors, these chips find applications in various fields such as processing and memory functions within servers. Wafer scale chips are highly efficient and have a lower power consumption compared to traditional smaller chips. They also offer higher performance and are more cost-effective to produce but are more complex to design and manufacture.
Train Meta’s Llama in just 1 day
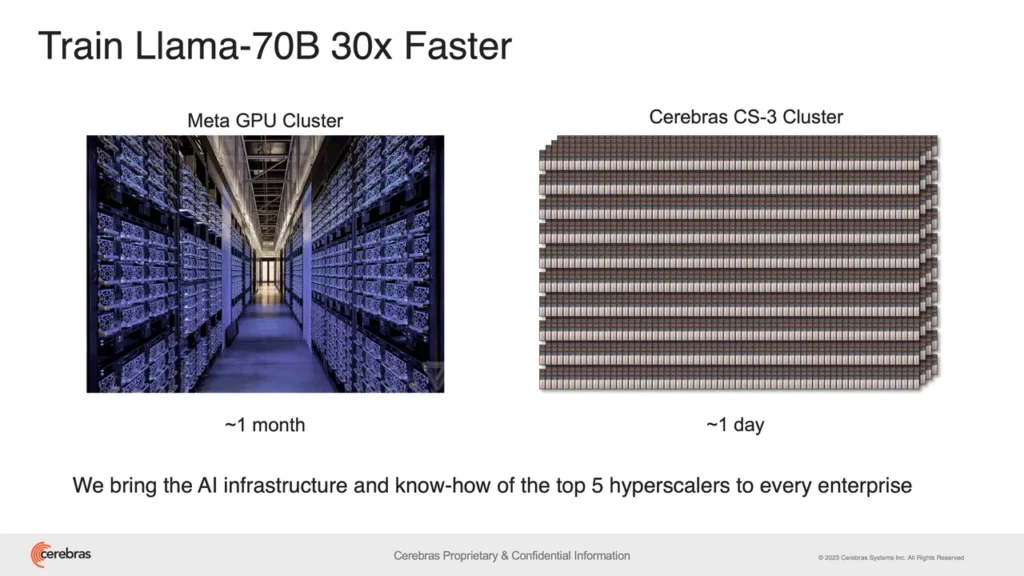
Cerebras argues that their system requires significantly less code to train models compared to traditional methods using Graphics Processing Units (GPUs). Also the WSE-3 can train models similar to Meta’s LLM, Llama 2, in just one day. This is a dramatic improvement compared to traditional methods that can take upwards of 30 days. This drastic reduction in training time translates to faster development cycles for AI applications, from drug discovery and materials science to autonomous vehicles and financial modeling.
AI supercomputer in making
Cerebras and G42 are strategically partnering to expand by constructing the Condor Galaxy 3, an AI supercomputer that will feature 64 CS-3 systems, boasting a staggering 57,600,000 cores.
Together, the two companies have already created two of the biggest AI supercomputers in the world: the Condor Galaxy 1 (CG-1) and the Condor Galaxy 2 (CG-2), which are based in California and have a combined performance of 8 ExaFLOPs. This partnership aims to deliver tens of exaFLOPs of AI compute, globally.
Advantages and disadvantages
One advantage Cerebras holds in the market is its exceptional ability to process vast amounts of data in remarkably short durations. Despite its rapid growth since its inception in 2016, reaching a valuation of over $4 billion, it remains a smaller player compared to the dominant AI hardware/software vendor, Nvidia.
Cerebras has primarily focused on training aspects of AI, which is just one facet in the broader landscape of AI applications. Nvidia, on the other hand, offers a multitude of offerings not only for training but also other products such as its CUDA classical-quantum platform, which has gained popularity among researchers and data scientists.
However, Cerebras is now expanding its scope beyond training. It recently announced plans to utilize its CS-3 AI accelerators to aid in training Qualcomm Technologies’ Cloud AI 100 Ultra system, aimed at accelerating inferencing tasks. This move positions Cerebras as a potential alternative to Nvidia’s inferencing systems, according to industry observers.
Another advantage for Cerebras lies in its ability to process Large Language Models (LLMs) within a single system, eliminating the need to scale thousands of GPUs. However, users would need to maintain continuous usage of the system to realize its full benefit in terms of return on investment.
Conclusion
Despite being a startup, Cerebras finds itself in a favorable position due to the high demand for generative AI. This demand currently outpaces the supply from Nvidia and other competitors, providing opportunities for companies like Cerebras in the AI offerings market.
The WSE-3 represents a significant leap forward in AI chip technology. The coming years will likely see a continued push for even more powerful and efficient AI hardware. This competition will ultimately benefit the entire AI ecosystem, leading to faster development of groundbreaking applications that will transform our world.