Introduction
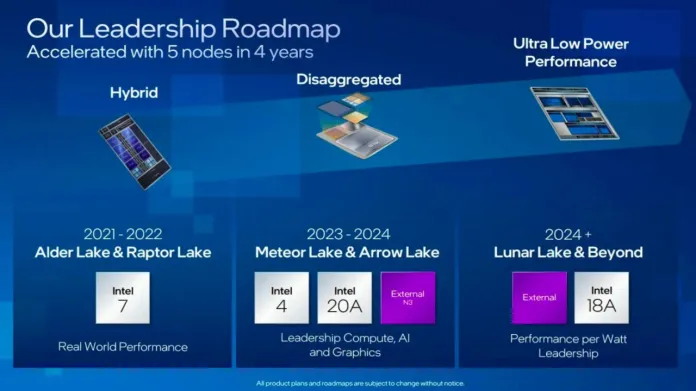
In the ever-evolving landscape of mobile computing, Intel has consistently strived to push the boundaries of performance, efficiency, and innovation. Their latest endeavor, the Lunar Lake CPUs, promises to redefine what users can expect from thin and light notebooks.
With a focus on maximizing performance per watt and integrating cutting-edge technologies, Lunar Lake sets a new standard for mobile processors.
Follow us on LinkedIn for everything around Semiconductors & AI
Performance leap: The 17W Intel Lunar Lake is expected to deliver a significant 50% improvement in multi-threaded performance compared to the 15W Meteor Lake CPU. This is impressive, especially considering the similar power consumption.
Focus on thin and light laptops: Intel Lunar Lake seems targeted towards thin and light laptops that prioritize high performance per watt for better battery life.
New architecture: It will likely use a combination of Lion Cove P-cores for demanding tasks and Skymont E-cores for handling background activities efficiently.
AI boost: Rumors suggest that Lunar Lake will also include a next-generation NPU (Neural Processing Unit) claiming a 3x performance improvement over Meteor Lake in AI tasks.
Graphics upgrade: The integrated graphics (iGPU) will reportedly be based on the new Xe2 “Battlemage” architecture, promising a 2x performance uplift compared to the current Xe architecture.
Limited availability: Expect Lunar Lake CPUs to launch in late 2024 with wider availability in early 2025.
Performance Boost with P-Core & E-Core Architecture for Intel Lunar Lake
One of the standout features of the Lunar Lake CPUs is the introduction of the P-Core & E-Core architecture.
The introduction of the P-Core (Performance Core) and E-Core (Efficiency Core) architecture in Lunar Lake CPUs represents a strategic approach to optimizing the balance between high-performance computing and power efficiency.
Lion Cove P-Cores: These cores are designed for high-performance computing tasks. They likely feature higher clock speeds, larger caches, and enhanced execution units optimized for tasks that demand maximum processing power. Applications such as gaming, content creation, and scientific simulations typically benefit from the increased performance provided by P-Cores.
Skymont E-Cores: E-Cores, on the other hand, focus on efficiency, optimizing tasks that prioritize power savings and energy efficiency over raw performance. These cores may have lower clock speeds and simpler execution units, but they excel in tasks that can be efficiently parallelized or don’t require intensive processing power. Examples include background tasks, browsing, video playback, and other everyday computing tasks where power efficiency is crucial, especially in portable devices like laptops and tablets.
Read More:NVIDIA Bans CUDA-Based Software On 3rd Party GPUs; Stirs China GPU Makers – techovedas
Multi-threaded Performance Breakthrough for Intel Lunar Lake
Several factors contribute to the significant improvement in multi-threaded performance observed in Lunar Lake CPUs, despite their having fewer threads compared to Meteor Lake counterparts.
Enhanced Core Design: The Lion Cove P-Cores and Skymont E-Cores in Lunar Lake CPUs likely feature improvements in microarchitecture, such as wider execution pipelines, larger caches, and better branch prediction mechanisms. These enhancements enable each core to handle multiple threads more efficiently, maximizing throughput even with fewer physical cores.
Improved Thread Scheduling and Resource Management: Lunar Lake CPUs may employ advanced thread scheduling algorithms and resource management techniques to better utilize the available cores. This includes optimizing thread placement and prioritization to minimize contention and maximize parallelism, resulting in improved multi-threaded performance across a variety of workloads.
Higher Clock Speeds and IPC: Lion Cove P-Cores and Skymont E-Cores might offer higher base and boost clock speeds compared to their predecessors, allowing them to execute instructions faster. Additionally, improvements in Instructions Per Clock (IPC) performance further enhance the efficiency of each core, enabling them to process more instructions per cycle and deliver higher overall multi-threaded performance.
Efficient Utilization of Limited Threads: Lunar Lake CPUs likely efficiently utilize the available threads, ensuring each thread is fully utilized without excessive context switching or idle time, despite their having fewer threads compared to Meteor Lake CPUs. This efficient thread utilization maximizes throughput and minimizes overhead, contributing to the observed increase in multi-threaded performance.
Overall, the remarkable improvement in multi-threaded performance demonstrated by Lunar Lake CPUs underscores the effectiveness of its core design, highlighting the formidable capabilities of Lion Cove and Skymont cores in efficiently handling a wide range of multi-threaded workloads.
Read More:NVIDIA Bans CUDA-Based Software On 3rd Party GPUs; Stirs China GPU Makers – techovedas
Looking Ahead
As Intel prepares to unveil Lunar Lake CPUs later this year, anticipation mounts regarding the impact they will have on the mobile computing landscape.
With advancements in performance, efficiency, and feature set, Lunar Lake represents a leap forward in Intel’s mobility CPU lineup.
Additionally, the integration of next-gen technologies like the Xe2 graphics architecture and enhanced NPU capabilities underscores Intel’s commitment to driving innovation and delivering superior computing experiences.
Read More:Court favors SK Hynix in Battle Against Former Worker’s Transfer to Micron – techovedas
Conclusion
In conclusion, Lunar Lake CPUs hold the promise of redefining mobile computing, offering users unparalleled performance, efficiency, and versatility in a compact and lightweight form factor.
Reference: Bionic_Squash on X




