Introduction
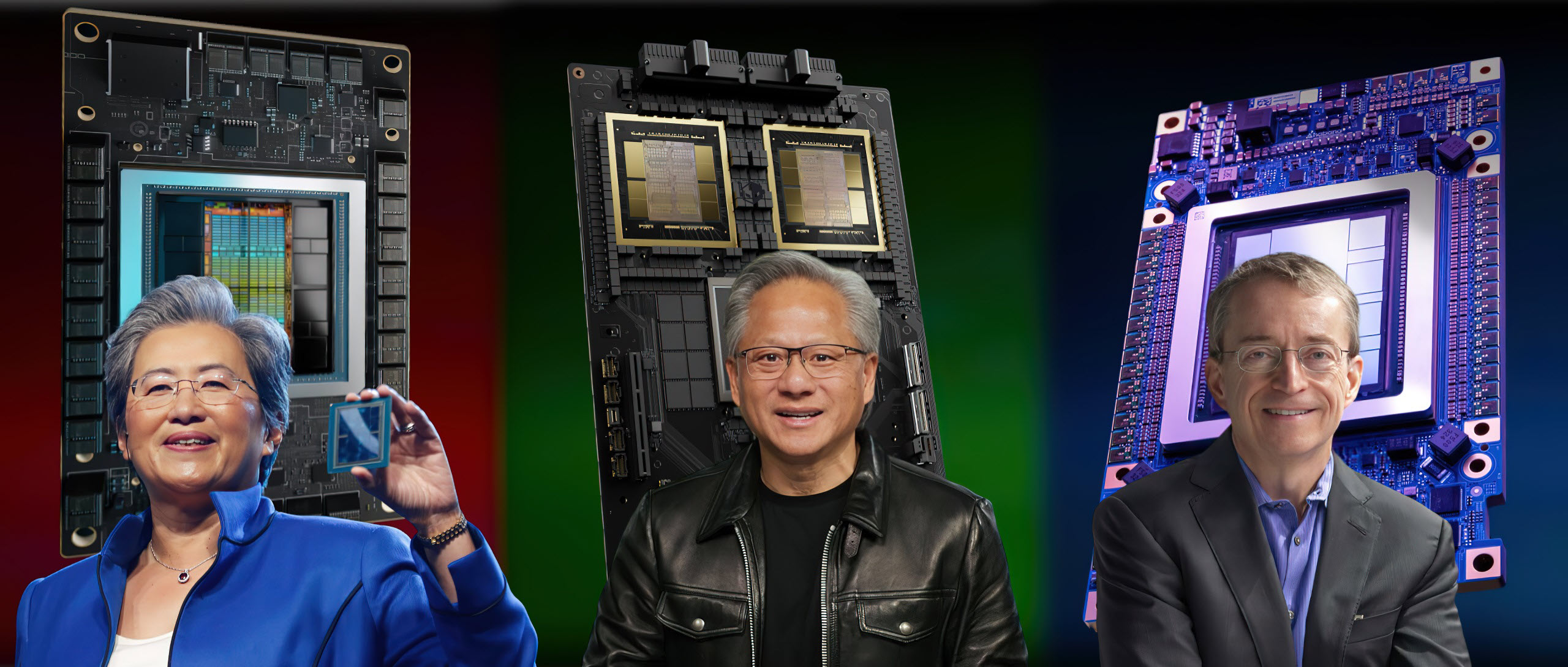
The semiconductor industry often referred to as the backbone of modern technology, is in the midst of an intense and ongoing battles for chip supremacy.
The rapid pace of innovation, coupled with the growing demand for more powerful and efficient chips, has led to fierce competition among industry giants.
Companies like Intel, TSMC, Samsung, and NVIDIA are constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible, striving to outdo each other in the race for technological dominance.
In this detailed analysis, we will explore the key Semiconductor battles that have shaped and continue to shape the semiconductor industry.
We will delve into the strategies employed by these leading companies, examine the technological advancements that are driving the industry forward, and analyze the market dynamics that influence their decisions.
From the development of cutting-edge process technologies to the strategic alliances and rivalries that define the industry, this article provides a comprehensive overview of the semiconductor battles that are shaping our technological future.
Follow us on Linkedin for everything around Semiconductors & AI
1. The AI Accelerator Arena: Nvidia vs. Everyone Else
The Battlefield:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is not just a buzzword; it’s revolutionizing industries from healthcare to finance. At the heart of this revolution are AI accelerators, specialized chips designed to handle complex AI computations efficiently.
Nvidia has carved out a dominant position with its Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), renowned for their parallel processing power.
The Challengers:
- AMD: With their Radeon Instinct line, AMD is pushing hard to catch up. Their GPUs are tailored for AI workloads, offering robust performance at competitive prices.
- Intel: Not to be left behind, Intel’s Xe GPUs (codenamed Ponte Vecchio) are designed to cater to AI and high-performance computing needs, marking a significant push into this lucrative market.
- Others: Companies like Google, with its Tensor Processing Units (TPUs), and newcomers like Cerebras Systems are also vying for a piece of the AI hardware market.
The Stakes:
Dominating the AI accelerator market means gaining a significant foothold in the future of technology. The winner here will influence AI development, driving advancements in machine learning, data analytics, and autonomous systems. Given AI’s potential to disrupt various industries, the stakes couldn’t be higher.
Read More: 7 Exciting Technology Products From CES 2024 – techovedas
2. Fab Supremacy: TSMC vs. Samsung vs. Everyone Else
The Battlefield:
Chip manufacturing, or fabrication, is a complex and capital-intensive process. TSMC (Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company) currently leads the pack with its cutting-edge fabrication technologies, producing the most advanced chips for tech giants like Apple and Nvidia.
The Challengers:
- Samsung: As TSMC’s primary competitor, Samsung is continually innovating to close the technological gap. They are investing heavily in their foundry business to offer competitive solutions.
- Global Investments: The US, China, and Europe are pouring resources into developing their own fabs to reduce reliance on Asian manufacturers. Initiatives like the US CHIPS Act aim to bolster domestic chip production capabilities.
The Stakes:
Control over fabs translates to control over the production of the world’s most critical chips. This semiconductor battles has significant geopolitical implications, influencing global supply chains and national security. Countries and companies that lead in semiconductor industry will dictate the pace and direction of technological advancement.
3. The CPU Power Struggle: Intel vs. AMD (Resurgence)
The Battlefield:
CPUs are the central processing units, essentially the “brains” of computers. Intel dominated this space for decades, but AMD’s Ryzen series has sparked a renaissance, challenging Intel’s hegemony with impressive performance and competitive pricing.
The Challengers:
- AMD: With their Ryzen processors, AMD has raised the bar by increasing core counts and optimizing performance, delivering excellent value across the board.
- Intel: In response, Intel is launching new architectures like Alder Lake and Sapphire Rapids, aiming to reclaim their leadership position by focusing on efficiency and multi-threaded performance.
The Stakes:
A strong presence in the CPU market means dominance in personal computing, gaming, and enterprise servers. This competition is driving innovation, pushing both companies to deliver better performance and value to consumers, ultimately shaping the future of computing.
Read More: 6 Reasons Why Nvidia Overtook Apple as World’s Second Most Valuable Company – techovedas
4. The Mobile Processor War: Qualcomm vs. Apple
The Battlefield:
Mobile processors are the engines behind our smartphones and tablets. Qualcomm’s Snapdragon chips have long powered Android devices, while Apple’s in-house designed A-series chips have set new standards in performance and efficiency.
The Challengers:
- Qualcomm: Continuously innovating, Qualcomm integrates AI and 5G capabilities into their Snapdragon processors, aiming to enhance user experiences and connectivity.
- Apple: With the A-series chips, Apple has achieved remarkable performance gains, making iPhones and iPads some of the most powerful mobile devices available.
- Others: MediaTek is also making strides, offering competitive alternatives to Qualcomm in the Android market.
The Stakes:
Winning the mobile processor war means influencing the entire mobile ecosystem, from app development to user experience. This semiconductor battles will determine which devices dominate the market and how they evolve, impacting billions of users worldwide.
5. The Emerging Memory Wars: DRAM & NAND Flash
The Battlefield:
Memory technologies like DRAM (Dynamic Random-Access Memory) and NAND Flash are essential for data storage and processing. DRAM is used for active tasks, while NAND Flash is crucial for permanent storage.
The Challengers:
- Samsung: Leading in both DRAM and NAND Flash production, Samsung continues to push the envelope in memory density and speed.
- SK Hynix and Micron: These companies are formidable competitors, investing heavily in research and development to enhance memory performance and capacity.
- China: Investing aggressively to build a self-sufficient semiconductor industry, aiming to reduce reliance on foreign technology.
The Stakes:
Advancements in memory technology are crucial for faster computers, advanced smartphones, and efficient data centers. The competition in this space drives innovation, leading to better performance, higher capacity, and more energy-efficient memory solutions.
Follow us on Linkedin for everything around Semiconductors & AI
6. The Gallium Nitride (GaN) Revolution
The Battlefield:
Silicon has been the dominant material for transistors for decades. However, Gallium Nitride (GaN) offers superior performance for high-power applications like radio frequency (RF) chips and power electronics.
The Challengers:
- Qorvo, Wolfspeed, and EPC: These companies are leading the charge in GaN technology. Despite its advantages, GaN is still more expensive to manufacture than silicon, which poses a challenge for widespread adoption.
The Stakes:
Widespread adoption of GaN could lead to more efficient power electronics, smaller and more powerful RF chips for 5G and beyond, and advancements in areas like electric vehicles. This shift could redefine the capabilities and efficiency of a wide range of electronic devices.
7. The Analog Renaissance
The Battlefield:
While digital technology has dominated recent advancements, there’s a renewed interest in analog chips, which handle real-world signals like sound and light.
The Challengers:
- Texas Instruments and Analog Devices: These companies are investing heavily in analog chip development. The trend is driven by the growing need for mixed-signal devices that combine both digital and analog functionality.
The Stakes:
A strong analog chip industry is crucial for the development of next-generation sensors, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and wearable technology. These devices require efficient and precise analog-to-digital conversion to function optimally.
8. The Photonics vs. Electronics Showdown
The Battlefield:
Traditionally, electrical signals have carried information within chips. However, photonics uses light to transmit data, offering potential advantages in speed and efficiency.
The Challengers:
- Intel and IBM: These companies are heavily invested in integrating photonic components with traditional electronics, aiming to revolutionize data transmission within chips and between them.
The Stakes:
Photonics could lead to faster computers and more efficient data centers by significantly improving data transmission speeds and reducing energy consumption. This technology has the potential to break current performance barriers in computing.
9. The Battle for Advanced Packaging
The Battlefield:
As transistors shrink further, chipmakers are exploring ways to stack multiple chips together in innovative packages, creating more powerful and efficient devices.
The Challengers:
- TSMC and Samsung: These companies are developing advanced packaging technologies like Fan-Out Wafer-Level Packaging (FOWLP) and Heterogeneous Integration, pushing the boundaries of miniaturization and performance.
The Stakes:
Advanced packaging allows for increased functionality in smaller devices, enabling the creation of more powerful and compact electronics. This innovation is critical for the continued progression of Moore’s Law.
10. The Rise of Specialized Processors
The Battlefield:
The “one-size-fits-all” CPU approach is being challenged by the development of specialized processors for specific tasks. These processors offer better performance and lower power consumption for specific applications.
The Challengers:
- Google with TPUs and Nvidia with GPUs: These companies are leading the way in creating specialized processors for AI workloads and graphics processing, respectively.
The Stakes:
Specialized processors can accelerate innovation in areas like AI, machine learning, and high-performance computing. This specialization allows for more efficient and powerful computation tailored to specific tasks, driving semiconductor battles against technological advancements in these fields.