Introduction
In a surprising announcement, Intel has disclosed a staggering $7 billion operating loss within its chip-making unit. This revelation signals potential challenges and underscores the increasing pressures faced by the tech giant in the competitive semiconductor industry.
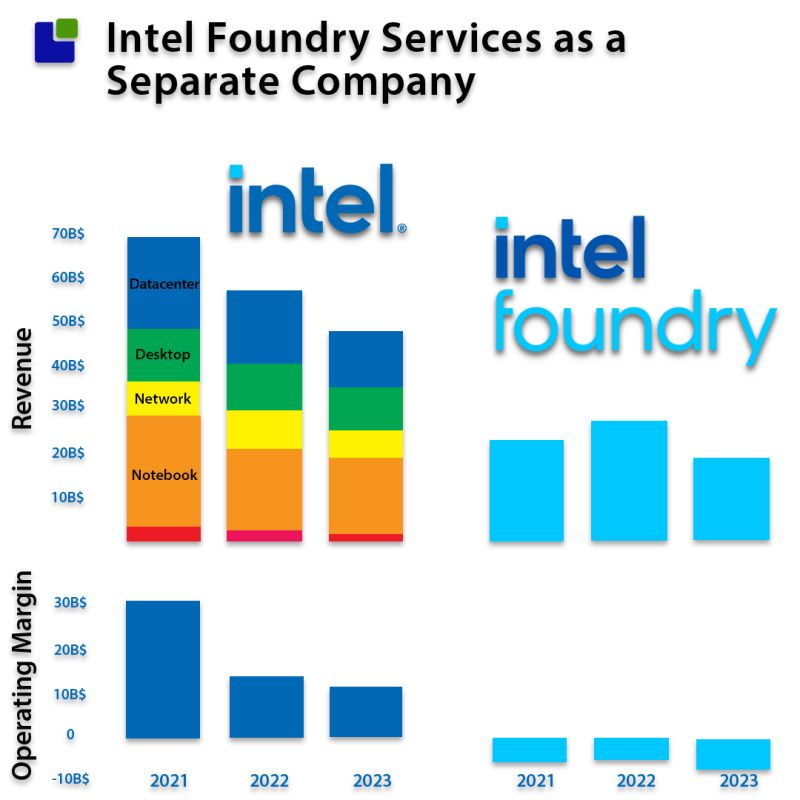
The company’s foundry business, crucial for producing cutting-edge chips, has been grappling with deepening operating losses, as revealed in its recent disclosures to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
These setbacks underscore Intel’s urgent need to regain ground lost to competitors like Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC).
Follow us on Linkedin for everything around Semiconductors & AI
Operating Losses and Revenue Decline:

Image Credits: Semiconductor Business Intelligence
Intel reported a substantial increase in operating losses for its manufacturing unit in 2023, amounting to $7 billion, compared to $5.2 billion in the previous year.
Concurrently, the unit’s revenue declined by 31%, falling from $27.49 billion to $18.9 billion. These figures highlight the magnitude of the challenges facing Intel’s foundry business.
Read More: 7.2 Magnitude Earthquake Hits Taiwan: TSMC and UMC Affected – techovedas
Market Response:
Following the SEC filing, Intel shares experienced a 4.3% decline, reflecting investor concerns about the company’s financial performance and competitive position within the semiconductor market.
Strategic Outlook:
During a presentation to investors, Intel’s Chief Executive Officer, Pat Gelsinger, acknowledged the severity of the situation, designating 2024 as the year with the highest operating losses for the chipmaking business.
However, Gelsinger expressed optimism about the company’s prospects, aiming to achieve operating breakeven by approximately 2027.
Read More: Want to Make a Career in VLSI: Master these 5 Engineering Subjects – techovedas
Identifying Challenges:
Gelsinger attributed the foundry business’s struggles to past decisions, including the reluctance to adopt advanced technologies such as extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography from ASML.
This choice hindered Intel’s competitiveness, as EUV machines offer cost-effectiveness and enhanced performance crucial for modern chip manufacturing.
Read More: Five Talks by Morris Chang Charting the Journey of TSMC
Adapting to Change:
Intel has taken steps to address its weaknesses. It outsources about 30% of its wafer production to external manufacturers like TSMC.
The goal is to decrease this dependency to around 20%. Intel is transitioning to EUV tools for enhanced efficiency and competitiveness.
Investment and Expansion:
In a bid to revitalize its chipmaking capabilities, Intel plans to invest $100 billion in constructing or expanding chip factories across four U.S. states.
This ambitious initiative underscores Intel’s commitment to reclaiming its position as a leading semiconductor manufacturer.
Read More: How Chaotic Were the First Six Months of NVIDIA Ft. Jensen Huang, CEO
Embracing Collaboration:
As part of its turnaround strategy, Intel intends to offer its manufacturing services to external companies, thereby leveraging its expertise and infrastructure.
This strategic shift reflects Intel’s recognition of the importance of collaboration and diversification in the highly competitive semiconductor landscape.
Conclusion:
Intel’s recent struggles underscore the challenges inherent in the semiconductor industry, characterized by rapid technological advancements and intense competition.
However, with a concerted effort to address past missteps, embrace innovation, and forge strategic partnerships, Intel remains poised to navigate these challenges and emerge stronger in the years ahead.
As Intel embarks on its journey of recovery, the company’s ability to execute its strategic vision and adapt to evolving market dynamics will be critical in determining its long-term success in the semiconductor industry.