Introduction
A revolutionary breakthrough is on the horizon. X-Silicon, a company comprised of seasoned engineers, has unveiled a RISC – V chip that merges CPU, GPU, and AI capabilities into a single core. This chip, dubbed the X-Silicon C-GPU, leverages the open-source RISC-V instruction set architecture (ISA) to create a hybrid out of a CPU and GPU.
Unified Core: Unlike traditional processors with separate CPU, GPU, and AI cores, X-Silicon’s chip merges everything into a single core. This could lead to:
- Improved Efficiency: By eliminating the need for separate cores and data transfer between them, the chip could be more efficient.
- Lower Power Consumption: A simpler design might use less power.
In this blog post, we delve into the intricacies of this innovative technology, breaking down technical terms and exploring its potential impact on the future of computing.
Follow us on Linkedin for everything around Semiconductors & AI
Understanding RISC-V
Before delving into the specifics of the X-Silicon C-GPU, let’s first grasp the fundamentals of RISC-V. RISC-V stands for Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC) – Five, denoting the fifth iteration of the RISC architecture. Unlike proprietary architectures like ARM, RISC-V is an open-source ISA, freely available for anyone to use and implement. It is designed to be low-power and scalable, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from embedded systems to high-performance computing.
Read more The Story of RISC-V – techovedas
The X-Silicon C-GPU
At the heart of X-Silicon’s innovation lies the integration of CPU, GPU, and AI capabilities within a single core. This isn’t like the typical designs from Intel and AMD where there are separate CPU cores and GPU cores. Instead, the core itself is designed to handle both CPU and GPU tasks. This new CPU/GPU hybrid was designed visioning a “jack of all trades” processor.
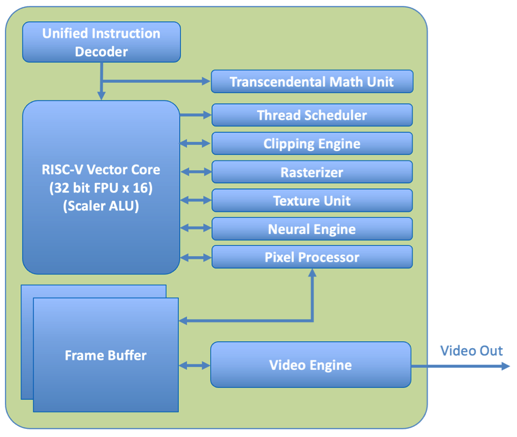
In order to reinvent the GPU shader core, X-Silicon created a new scalable RISC-V Vector Core acting as unified computer-graphics engine (C-GPU)
X-Silicon’s secret sauce lies in their C-GPU (CPU-GPU) architecture which combines a RISC-V CPU core with several key features:
- RISC-V Vector Core: This core handles both regular integer and floating-point instructions efficiently and is equipped with multiple processing units.
- Unified Instruction Decoder: A single decoder feeds instructions to the different parts of the core, streamlining the process.
- Specialized Units: Integrated within the core are a thread scheduler, texture unit, rasterizer, clipping engine, neural engine, and pixel processors. These handle tasks specific to graphics, AI, and video processing.
- NanoTile Architecture: This allows for additional AI acceleration capabilities within the same core.
Here’s how these features come together:
- Single Instruction Stream: By using a single RISC-V ISA for both CPU and GPU operations, the chip avoids the need for separate instruction sets and memory spaces. This reduces complexity and potentially improves efficiency.
- Direct Hardware Access: Components like the neural engine and vector units can directly access hardware registers within the core, enabling faster processing compared to traditional architectures that rely on data movement between cores.
Overall, X-Silicon’s design merges functionalities typically found in separate cores into a single unit. This offers potential benefits in terms of efficiency, power consumption, and potentially lower memory footprint.
Multiple C-GPU cores can be combined and connected using an on-chip fast compositor fabric that can dynamically aggregate outputs from each core into a common buffer—i.e., frame buffer for graphics use cases or pipelined buffers for codec, video effects processing, and AI processing, as illustrated in the following diagram.

Key Technical Features
The X-Silicon C-GPU architecture boasts several key technical features that set it apart:
CPU-with-GPU RISC-V ISA: The chip utilizes a specialized RISC-V instruction set that combines CPU and GPU capabilities. This allows for efficient execution of both CPU and GPU tasks within the same core.
NanoTile Architecture: C-GPU features a patented NanoTile architecture, which combines real-time processing with graphical rendering to efficiently manage compute resources. Moreover, NanoTile is said to contribute significantly to AI/ML applications, due to the optimized data flow, potentially creating it a viable alternative to the modern-day NPU offerings
Vulkan Support: The C-GPU offers Vulkan support, facilitating compatibility with Android platforms. This opens up opportunities for seamless integration into mobile and embedded devices.
Vulkan is a specialized graphics API, similar to a language, that helps video games and apps talk to your device’s graphics hardware.
What is X-Silicon?
X-Silicon is a company made up of ex-Silicon Valley engineers, founded in San Diego in 2022. Those engineers primarily come from AMD, Qualcomm, ATI Technologies, Intel, and Dell, and they set about reinventing a GPU shader core.
A GPU shader core is a component within a graphics processing unit (GPU) responsible for performing computations related to the visual aspects of objects in a scene.
The company claims that they have filed 14 patents while building their C-GPU architecture.
Benefits & Implications
The integration of CPU, GPU, and AI capabilities into a single core offers improved efficiency, crucial in today’s energy-conscious world.
The X-Silicon C-GPU consolidates CPU and GPU functionalities within a unified architecture, promising reduced power consumption and enhanced resource utilization.
This makes it ideal for battery-powered devices and environmentally sustainable computing solutions.
The chip’s ability to execute CPU and GPU tasks in parallel results in heightened computational capabilities and reduced latency.
This is particularly advantageous for real-time applications like gaming, multimedia processing, and artificial intelligence inference tasks.
Furthermore, the X-Silicon C-GPU holds implications for the broader landscape of innovation. As companies increasingly adopt this integrated architecture and leverage its capabilities, we can expect to witness a wave of innovation across various industries with C-CPU architecture.
Baselining the New product
Existing processor architectures typically have separate cores for CPU, GPU, and AI functionalities. Here’s a comparison of X-Silicon’s RISC-V chip with this traditional approach:
Traditional Architecture
- Separate Cores: Dedicated CPU, GPU, and AI cores, each with its own instruction set and memory space.
- Data Transfer: Requires data movement between cores, which can be slow and power-consuming.
- Complexity: Increased design complexity due to separate cores and data paths.
X-Silicon’s RISC-V Chip
- Unified Core: Merges CPU, GPU, and AI functionalities into a single core with a unified RISC-V ISA.
- Direct Hardware Access: Components can directly access hardware registers within the core, potentially faster than traditional data transfer.
- Simpler Design: Potentially lower power consumption and smaller footprint due to a unified core.
Here’s a table summarizing the key points:
| Feature | Traditional Architecture | X-Silicon’s RISC-V Chip |
|---|---|---|
| Core Design | Separate CPU, GPU, AI cores | Unified Core |
| Instruction Set | Separate for CPU, GPU, AI | Unified RISC-V ISA |
| Data Movement | Requires data transfer between cores | Direct hardware access within core |
| Complexity | More complex design | Potentially simpler design |
| Potential Benefits | High performance for specific tasks | Improved efficiency, lower power consumption, smaller footprint (all theoretical) |
In essence, X-Silicon’s design trades potential performance for overall efficiency and a smaller footprint. Whether this approach proves successful depends on real-world testing and how well the unified core handles diverse tasks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the X-Silicon C-GPU marks a paradigm shift in RISC-V chip architecture. It integrates CPU, GPU, and AI capabilities into a single core. Its promise lies in improved efficiency, enhanced performance, and versatility. This innovative chip has the potential to reshape the future of computing. As we await further developments and product releases, one thing is clear: the X-Silicon C-GPU will introduce the industry to a new processing architecture.



