Introduction:
The history of industry is a story of constant evolution and innovation. From the early days of mechanization powered by water and steam to the current era of interconnected smart systems, each industrial revolution has left an indelible mark on the way we produce goods.
In this blog post, we will delve into the four industrial revolutions, tracing the advancements in technology and focusing on the current Industry 4.0, using the example of the semiconductor industry to illustrate the transformative power of these revolutions.
Join TechoVedas Community here
Industry 1.0: The Age of Mechanization (Late 18th century to early 19th century)
The first industrial revolution laid the foundation for modern industry by introducing mechanized manufacturing processes.
Water and steam power fueled the rise of factories, replacing manual labor with machines. This shift from agrarian economies to industrial ones marked a pivotal moment in history, setting the stage for further innovations.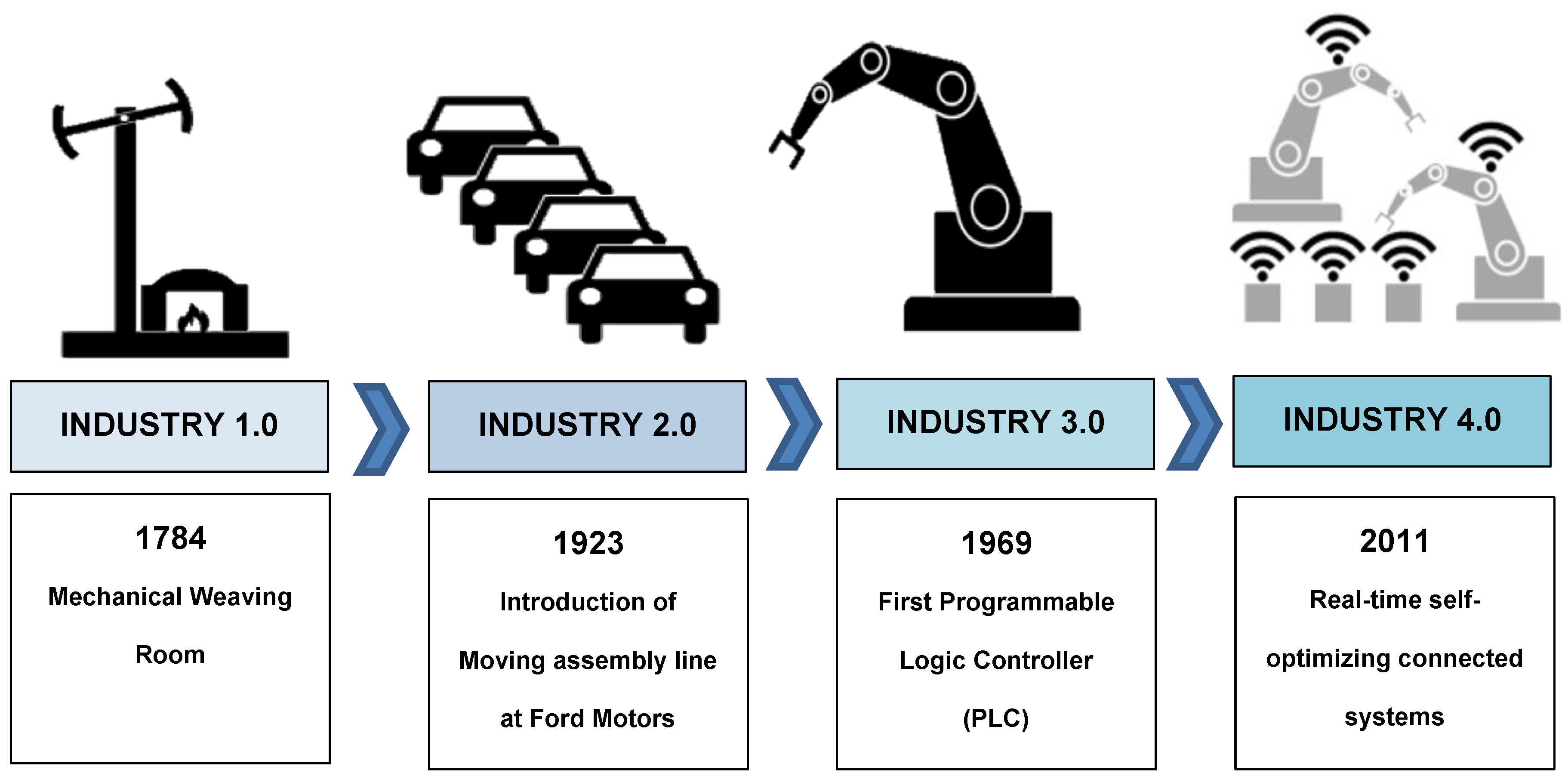
Industry 2.0: Electrification and Mass Production (Late 19th century to early 20th century)
The second industrial revolution brought about widespread electrification and the development of assembly lines.
Visionaries like Thomas Edison and Henry Ford played crucial roles in this era, introducing electricity to power factories and revolutionizing mass production techniques.
The increased efficiency and lower costs associated with this period laid the groundwork for the modern industrial landscape.
Read More: Samsung Paves the Way for AI-Driven, Human-Free Production by 2030 – techovedas
Industry 3.0: Computerization and Automation (Late 20th century)
The third industrial revolution witnessed the advent of computerization and automation. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and computer-aided design/manufacturing (CAD/CAM) became integral to manufacturing processes.
Automation improved precision, efficiency, and the ability to handle complex tasks, marking a significant leap forward in industrial capabilities.
Part 3- India’s semiconductor dream: Failed proposals & outdated SCL(2006-2022)
Industry 4.0: The Digital Age (Current and ongoing)
We find ourselves in the midst of Industry 4.0, where the integration of digital technologies is transforming industries at an unprecedented pace. The pillars of Industry 4.0 include the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), big data, and cyber-physical systems. These technologies are interconnected, allowing machines and processes to communicate, analyze data in real-time, and make informed decisions.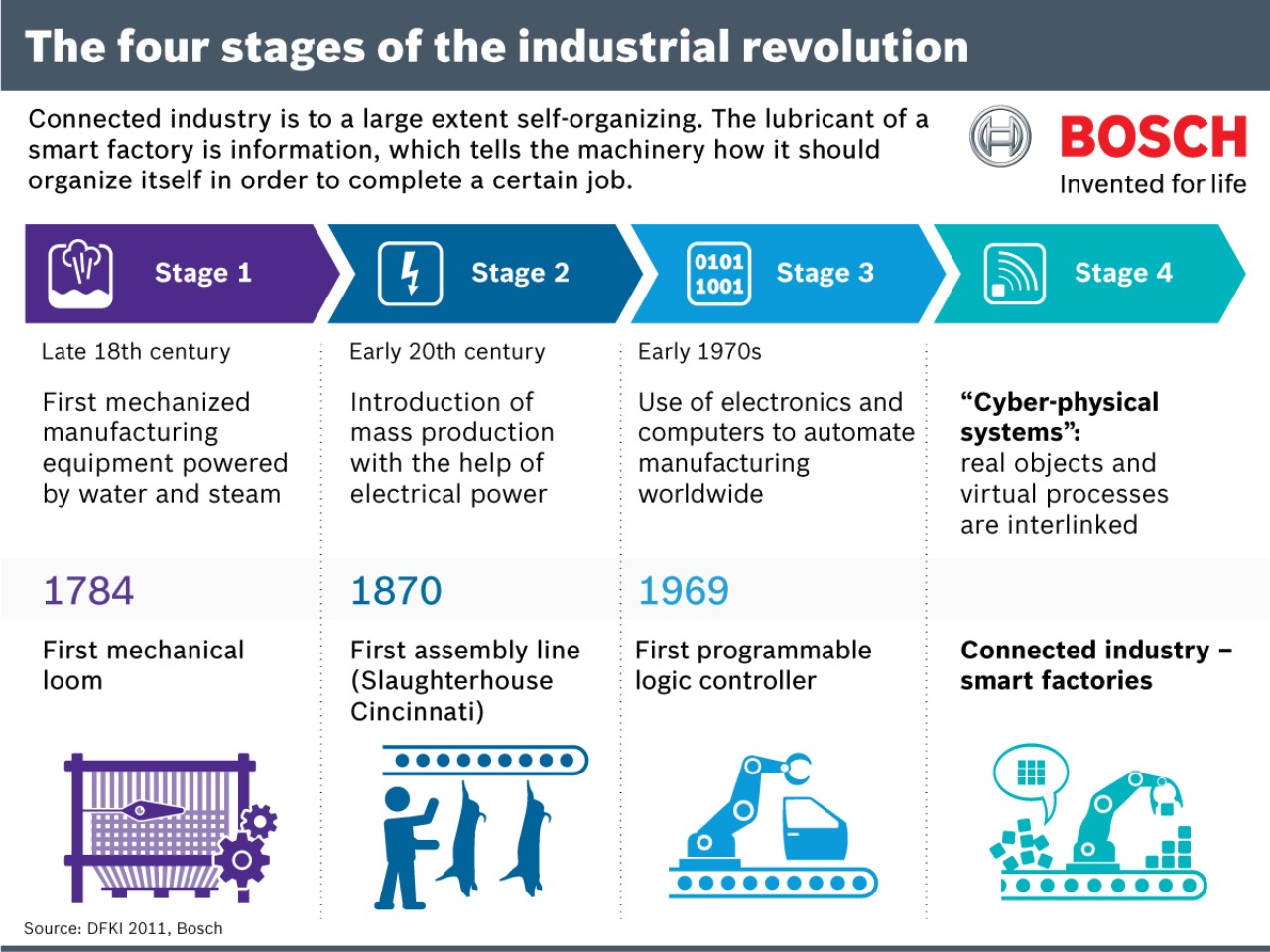
Semiconductors in Industry 4.0:
The semiconductor industry serves as a compelling example of how Industry 4.0 technologies are reshaping manufacturing. Semiconductors are the backbone of modern electronics, and their production has evolved significantly in recent years.
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices are embedded in semiconductor manufacturing equipment to gather real-time data on production processes. This data helps in predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and increasing overall efficiency.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is employed in semiconductor design and production to enhance decision-making processes. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to optimize chip designs, improve manufacturing yields, and streamline production workflows.
Big Data: The semiconductor industry deals with massive amounts of data during the manufacturing process. Big data analytics enables companies to extract valuable insights, identify patterns, and optimize production parameters for better quality and efficiency.
Cyber-Physical Systems: In semiconductor manufacturing, cyber-physical systems integrate the virtual and physical aspects of production. This ensures a seamless connection between design software, manufacturing equipment, and quality control systems, creating a more synchronized and efficient production environment.
Read More: Explained: What The Hell Is Internet of Things (IoT)? – techovedas
Conclusion:
The journey from Industry 1.0 to Industry 4.0 is a testament to humanity’s ability to adapt, innovate, and embrace technological advancements. The semiconductor industry exemplifies how these revolutions have not only shaped the manufacturing landscape but have also paved the way for a future where digital technologies continue to drive progress. As we stand on the cusp of further breakthroughs, Industry 4.0 promises a future where the boundaries between the physical and digital worlds blur, creating a more interconnected, intelligent, and efficient industrial ecosystem.



