Introduction
There is one term that is making the life of a semiconductor design engineer easier. This term is so versatile that it has a business model today.-IP cores.
In semiconductor design, an IP core, short for Intellectual Property core, is a pre-designed and reusable block of logic or functionality that serves as a building block for creating complex chips. Think of them like Lego bricks for chip design!
IP cores are the digital building blocks which overlooked by the end-user, play a pivotal role in shaping the functionality and efficiency of any processor that comes out in the market. This article delves deep into the essence of IP cores, their types, advantages and challenges. From the fundamental distinction between soft and hard to exploring the competitive landscape of the semiconductor IP market, we’ll uncover the role these blocks play in driving innovation and progress in the semiconductor industry.
Follow us on Linkedin for everything around Semiconductors & AI
What are IP cores?
They are like ready-made pieces of a puzzle that chip designers can license to use in their own designs.
As technology advances, chips are becoming more complex, packing numerous functions into a single unit, known as System on Chip (SOC) designs. In these designs, pre-designed IP cores play a crucial role as they provide essential building blocks for various functions.
Functionality: An IP core can represent various functionalities, including digital logic (performing calculations), analog circuits (processing continuous signals), or even an entire sub-system like a memory controller or a communication interface.
Reusability: The key benefit of IP cores is reusability. Designers can incorporate these pre-verified blocks into their chip designs instead of reinventing the wheel for every single function. This saves significant time and effort.
Licensing: IP cores can be licensed from third-party vendors or developed in-house by a company for its own use.
Read more What is a Network on Chip Vs System on Chip? – techovedas
Types by core
There are two main types of IP cores: soft IP cores and hard IP cores.
Designers create soft IP cores using HDLs (Hardware Description Languages) like Verilog or VHDL. Conversely, designers craft hard it is using physical design techniques and typically deliver them as physical layout databases.
Soft IP cores – crafted using hardware description languages (HDLs) like Verilog or VHDL, are usually provided as synthesizable source code. This means designers can adjust and tailor them to meet their unique needs.Their value lies in their flexibility and adaptability. It is making them well-suited for diverse applications.

Example – Soft processor IP cores, like the ARM Cortex-M series or RISC-V cores, offer programmable computing capabilities that designers can customize for various applications.Designers can adjust parameters like clock speed, cache size, and instruction set architecture to meet specific performance and power requirements.
Hard IP cores -It employ physical design techniques and are often delivered as pre-made physical layouts or netlists. They optimize for performance, power usage, and size, ensuring high efficiency and reliability. However, they offer less flexibility compared to soft IP cores.
Example – example of a hard IP core is the SerDes block. SerDes is a key component in high-speed communications to enable rapid data transfer. It converts data between serial and parallel interfaces bidirectionally. The purpose of this process is to provide a high-speed data path.
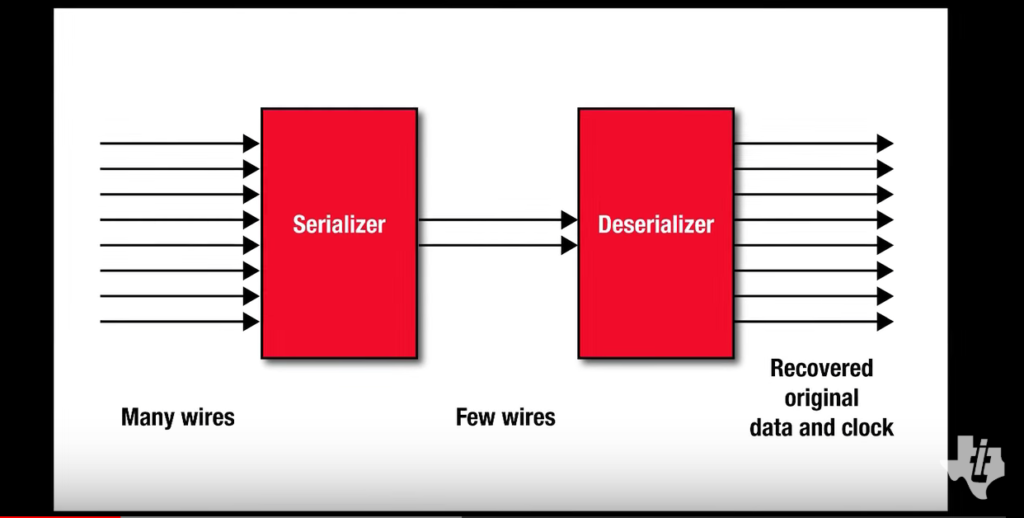
A SerDes block is often provided as a hard macro by semiconductor vendors. This means the physical layout, including transistors, wires, and other components, is already optimized for a specific manufacturing process.
What is Semiconductor IP business?

The Semiconductor Intellectual Property (IP) Market is where pre-designed and pre-verified blocks are bought and sold for use in applications.
The Semiconductor IP Market is highly competitive, with several key players offering a wide range of IP components and solutions. These players include semiconductor IP vendors, IP design houses, and foundries. They compete based on factors such as the breadth and quality of their IP portfolio, technological expertise, customer support, and pricing strategies.
Major Player in Semiconductor Intellectual Property (IP) Market:
- Arm
- Synopsys
- Cadence Design Systems
- Rambus
- Marvell Technology Group
Read more 7 Key Drivers of Thriving Global Semiconductor Market – techovedas
Advantages
The adoption of IP cores brings several benefits to semiconductor design:
Accelerated development: By leveraging pre-designed IP cores, designers can significantly reduce development time and effort, allowing them to focus on differentiation and innovation.
Cost-effectiveness: Reusing it eliminates the need to reinvent the wheel for common functionalities, resulting in lower development costs and higher return on investment.
Quality and reliability:It is developed by specialized vendors undergo rigorous testing and validation, ensuring high quality and reliability in semiconductor designs.
Challenges and Considerations
Integration challenges: Integrating multiple IP cores from different vendors into a single design can be complex, requiring careful coordination and compatibility testing.
Verification and testing: Ensuring the functionality and reliability of integrated its demands thorough verification and testing procedures, including simulation, emulation, and prototyping.
Licensing and legal considerations: The use of third-party IP cores entails legal considerations such as licensing agreements, intellectual property rights, and compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Conclusion
In conclusion,it serve as the foundation upon which modern semiconductor designs are built. From processors to interfaces, memories to analog components, these pre-designed building blocks accelerate development, reduce costs, and enhance the quality and reliability of electronic devices. As the semiconductor industry evolves, it will continue to play a vital role in driving innovation and progress, powering the next generation of electronic products and technologies