Introduction:
Intel’s relentless pursuit of innovation in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) has reached new heights with the introduction of the Intel Gaudi 3 AI accelerator. Intel is looking to take market share from current leader Nvidia, which has an estimated 80% of the AI chip market.
Intel released their latest AI chip, the Gaudi 3, on Tuesday. This chip is designed to compete directly with Nvidia’s currently dominant H100 chip. Intel claims the Gaudi 3 is twice as power-efficient and can run AI models 1.5 times faster than the H100. This news caused Nvidia’s stock to dip as investors reacted to the increased competition.

Intel shares moves up While Nvidia goes down
In this blog post, we delve into the groundbreaking features of the Intel Gaudi 3 accelerator, its significance for enterprise AI adoption, and how it outperforms competitors like the Nvidia H100 at a fraction of the cost.
Follow us on Linkedin for everything around Semiconductors & AI
Intel Gaudi 3: Redefining AI Acceleration
The Intel Gaudi 3 AI accelerator marks a significant milestone in AI inference technology, building upon the success of its predecessor, the Gaudi 2 accelerator. 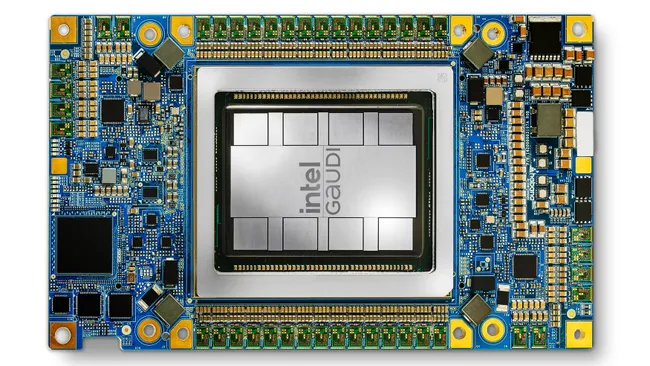
Designed for efficient large-scale AI compute, the Gaudi 3 accelerator boasts impressive advancements, including a 4x increase in AI compute for BF16, 1.5x higher memory bandwidth, and 2x networking bandwidth compared to its predecessor. These enhancements translate into substantial improvements in performance and productivity for AI training and inference tasks, particularly on large language models (LLMs) and multimodal models.
In the ever-evolving landscape of the AI market, a significant gap persists in the current offerings. Feedback from our customers and the broader market underscores a desire for increased choice. Enterprises weigh considerations such as availability, scalability, performance, cost, and energy efficiency. Intel Gaudi 3 stands out as the GenAI alternative presenting a compelling combination of price performance, system scalability, and time-to-value advantage.”
–Justin Hotard, Intel executive vice president and general manager of the Data Center and AI Group
Diving deeper into Intel’s Gaudi 3 and the AI chip race
Gaudi 3 Specs and Performance:
- Architecture: Successor to Gaudi 2, built on the foundation of Intel’s acquisition of Habana Labs in 2019.
- Focus: Designed for enterprise AI applications, specifically generative AI (GenAI) which requires high performance.
- Performance Claims:
- Intel claims Gaudi 3 delivers 50% better inference (running AI models) and 40% better power efficiency compared to Nvidia’s H100.
- It achieves this through a combination of factors including:
- Dual-die Design: Each Gaudi 3 chip has two processing dies, packing more processing power.
- Tensor Processing Cores: Features 64 fifth-generation Tensor Processing Cores (TPCs) specifically designed for AI workloads.
- High Bandwidth Memory: Utilizes 128GB of HBM2e memory stacked on the chip for faster data access.
- Networking: Doubles the Gaudi 2’s Ethernet connectivity with 24x 200Gbps RoCE controllers for high-speed communication within a system and between nodes in a cluster.
- Availability:
- Gaudi 3 is currently being sampled to partners and is expected to be in high-volume production by Q3 2024.
- It will be available in pre-built systems from OEMs like Dell, HPE, Lenovo, and Supermicro.
- Intel will also offer Gaudi 3 systems in their Developer Cloud for easier testing and adoption.
Challenges for Gaudi 3:
- Software Ecosystem: Nvidia has a significant advantage with their CUDA programming platform, widely used by developers for AI applications. Intel is working on open-source software alternatives but may need time to catch up.
- Market Share: Nvidia currently holds a dominant position in the AI chip market. While Gaudi 3 offers compelling performance and cost benefits, it needs to win over developers and establish itself in the market.
The AI Chip Race Heats Up:
- This launch intensifies the competition in the AI chip market, which benefits everyone.
- With more players like Intel and AMD (who introduced their data center GPU last year) joining the race, we can expect faster innovation and potentially lower prices for AI hardware.
- The focus is shifting towards offering not just powerful chips but also comprehensive AI software solutions to attract developers and businesses.
Overall, the Gaudi 3 is a significant step forward for Intel in the AI chip race. Its performance and power efficiency claims are impressive, but software compatibility and market adoption remain key challenges. This competition will ultimately lead to better AI tools and capabilities for various industries.
Choice and Flexibility: Open Community-Based Software and Industry-Standard Networking
Recognizing the need for flexibility and openness in AI infrastructure, Intel offers customers a choice with the Gaudi 3 accelerator.
By providing open community-based software and industry-standard Ethernet networking, Intel empowers enterprises to scale their AI systems more flexibly and efficiently.
This approach not only fosters innovation but also eliminates vendor lock-in, enabling businesses to tailor their AI infrastructure to meet specific requirements while optimizing cost and performance.
Unmatched Performance and Efficiency: The Architecture of Intel Gaudi 3
At the heart of the Intel Gaudi 3 accelerator lies a custom architecture optimized for high-performance, high-efficiency GenAI compute.
Moreover, featuring a heterogenous compute engine comprising 64 AI-custom and programmable Tensor Processor Cores (TPCs) and eight Matrix Multiplication Engines (MMEs), the Gaudi 3 accelerator excels in handling complex matrix operations fundamental to deep learning algorithms.
Additionally, with 128GB of HBMe2 memory capacity and 3.7TB/s memory bandwidth, the Gaudi 3 accelerator effortlessly processes large GenAI datasets, enhancing workload performance and data center cost efficiency.
Read More: 4 Ways AI-Powered NPUs Are Taking Games to the Next Level – techovedas
Cost-Effective Cloud Solutions and Market Adoption
The Intel Gaudi 3 accelerator is not just a technological marvel but also a cost-effective solution for enterprises seeking to deploy AI infrastructure at scale.
With notable OEM adopters like Dell Technologies, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Lenovo, and Supermicro, the Gaudi 3 accelerator is poised to drive widespread market adoption.
Moreover, by powering cost-effective cloud LLM infrastructures, such as those utilized by NAVER, Intel extends its reach to organizations looking to leverage AI for innovation and growth.
Read more 3 Most Anticipated Graphic Card Launches of 2024 – techovedas
Challenges for Gaudi 3
Software Ecosystem: Nvidia has a significant advantage with their CUDA programming platform, widely used by developers for AI applications. Intel is working on open-source software alternatives but may need time to catch up.
Market Share: Nvidia currently holds a dominant position in the AI chip market. While Gaudi 3 offers compelling performance and cost benefits, it needs to win over developers and establish itself in the market.
Future Directions: Accelerating AI with Falcon Shores
Looking ahead, Intel’s momentum in AI acceleration will continue with the introduction of Falcon Shores, the next-generation graphics processing unit (GPU) for AI and high-performance computing (HPC).
Integrating Intel Gaudi and Intel® Xe intellectual property (IP) with a single GPU programming interface built on the Intel® oneAPI specification, Falcon Shores represents the next frontier in AI acceleration, further advancing the capabilities and scalability of Intel’s AI solutions.
Read More: 5 High Growth Stocks From the World of Semiconductors – techovedas
Intel Gaudi 3 vs Nvidia H100 in Enterprise AI:
Intel’s latest innovation, the Gaudi 3 AI accelerator, surpasses Nvidia’s H100 in enterprise AI performance, heralding a new era in AI acceleration.
Here’s a side-by-side comparison of Intel’s Gaudi 3 and Nvidia’s H100 to help you see how they stack up:
| Feature | Intel Gaudi 3 | Nvidia H100 |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Successor to Gaudi 2, 5nm process | Ampere architecture, 7nm process |
| Focus | Enterprise AI, Generative AI (GenAI) | High-performance computing, AI, graphics |
| Performance Claims | * 50% faster inference | * Competitive performance across various AI tasks |
| * 40% better power efficiency | * Lower power efficiency for some workloads | |
| * Up to 1.7x faster time-to-train (Intel claim) | * Training performance varies based on workload | |
| Key Technologies | * Dual-die design | * Single-die design |
| * 64 fifth-gen Tensor Processing Cores (TPCs) | * Nvidia Tensor Cores | |
| * 128GB HBM2e memory | * HBM2e memory (capacity not publicly available) | |
| * 24x 200Gbps RoCE controllers | * Networking capabilities not publicly detailed | |
| Availability | * Sampling to partners, Q3 2024 high-volume production | * Currently available |
| Software Ecosystem | * Developing open-source alternatives to CUDA | * Established CUDA platform with wide developer adoption |
| Market Share | * New entrant vying for market share | * Dominant player in the AI chip market |
Here’s a quick breakdown of the key differences:
- Performance: Intel claims Gaudi 3 offers faster inference and better power efficiency, but Nvidia might still hold an edge in specific workloads. Training performance benchmarks are yet to be independently verified.
- Technology: Gaudi 3 utilizes a dual-die design and newer 5nm process technology for potentially higher efficiency. Nvidia’s H100 boasts a single-die design but with a proven track record.
- Software: Nvidia has a significant advantage with their CUDA programming environment. While Intel is working on alternatives, developer adoption might take time.
- Availability: Nvidia’s H100 is currently available, while Gaudi 3 is still in the sampling phase with partners.
Choosing between them depends on your needs:
- If raw power and established software support are priorities, Nvidia’s H100 might be the better choice (for now).
- If power efficiency and potentially faster inference are crucial, and you’re open to exploring new software options, Gaudi 3 could be a compelling alternative.
It’s still early days for Gaudi 3, and independent benchmarks will be crucial in determining its true performance compared to H100. The competition is heating up, which will ultimately benefit users with faster advancements and potentially lower costs for AI hardware.
Choosing between them depends on your needs:
- If raw power and established software support are priorities, Nvidia’s H100 might be the better choice (for now).
- If power efficiency and potentially faster inference are crucial, and you’re open to exploring new software options, Gaudi 3 could be a compelling alternative.
Read more AMD vs Intel: Which CPU Reigns Supreme in 2024? – techovedas
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Intel Gaudi 3 AI accelerator represents a quantum leap in AI acceleration technology, offering unparalleled performance, efficiency, and choice for enterprise GenAI applications.
Additionally,With its innovative architecture, open ecosystem, and cost-effective solutions, the Gaudi 3 accelerator is poised to catalyze the widespread adoption of AI across industries, fueling innovation, and driving business growth.
As enterprises embrace the transformative power of AI, Intel stands at the forefront, delivering the tools and technologies to power the AI-driven future.