Introduction:
The perpetual tug-of-war between AMD and Intel in the CPU arena has always kept tech enthusiasts on their toes.
Both juggernauts consistently endeavor to outshine each other in performance, efficiency, and innovation.
In this comprehensive analysis, we’ll delve into various aspects of AMD and Intel CPUs in 2024, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate the nuanced decision of selecting the optimal processor for your needs.
Follow us on Linkedin for everything around Semiconductors & AI
AMD vs. Intel: Which CPU is best?
AMD and Intel, two behemoths in the hardware industry, have long been engaged in a fierce rivalry, driving forward technological advancements and pushing the boundaries of CPU performance.
What is the difference between AMD and Intel CPU?
Architecture:
AMD’s Zen architecture, known for its modular design, emphasizes multi-threading and integrated graphics capabilities.
In contrast, Intel follows a more traditional monolithic approach, focusing on maximizing single-threaded performance.
This architectural distinction manifests in diverse performance characteristics and use-case scenarios.
Manufacturing Processes:
AMD’s utilization of 7nm technology in its manufacturing processes affords advantages in power efficiency and transistor density.
Meanwhile, Intel’s transition from 14nm to 10nm processes introduces complexities and impacts performance and capabilities in varying degrees.
AMD vs Intel: Pricing and Value
Pricing and Value Proposition:
AMD often offers competitive pricing, particularly in mid to high-end segments, delivering commendable value for performance.
On the other hand, Intel’s pricing strategy may fluctuate, with some models commanding premiums for features like reliability and compatibility.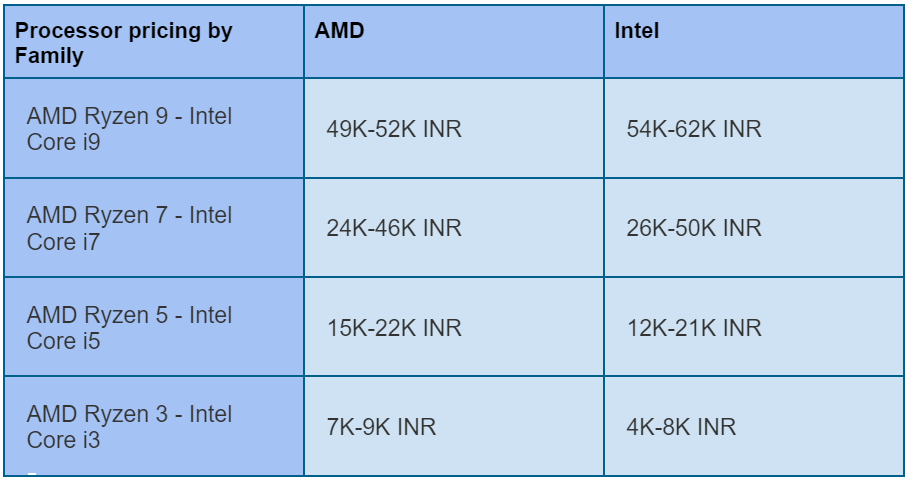
However, Intel’s diverse offerings cater to a wide spectrum of budgets and usage scenarios.
Read More: How Advanced Packaging is Merging Semiconductor Manufacturing and Packaging – techovedas
AMD vs Intel: Gaming Performance
Gaming Performance:
Intel’s Core i9-12900K and Core i7-12700K demonstrate formidable gaming capabilities, delivering high frame rates and smooth gaming experiences.
AMD vs Intel: Gaming Performance Comparison
| Aspect | AMD CPUs | Intel CPUs |
|---|---|---|
| Flagship Models | Ryzen 9 5900X, Ryzen 9 5950X | Core i9-12900K, Core i7-12700K |
| Mid-range Models | Ryzen 7 5800X, Ryzen 5 5600X | Core i5-12600K, Core i5-12400F |
| Gaming Performance | Excellent performance in multi-core optimized titles | Superior single-threaded performance; Strong in gaming |
| Overclocking | Generally stable overclocking; Limited headroom | Potential for significant overclocking; Enhanced tuning |
| Price-to-Performance | Competitive pricing; Good value for gaming enthusiasts | Premium pricing for flagship models; Varies across lineup |
In the realm of gaming performance, both AMD and Intel offer formidable options tailored to gamers’ preferences and budgets.
While AMD’s Ryzen CPUs excel in multi-core optimized titles, Intel’s offerings, particularly the Core i9 and Core i7 series, boast superior single-threaded performance, contributing to enhanced gaming experiences.
Overclocking capabilities vary between the two, with Intel CPUs often exhibiting greater headroom for significant overclocking.
However, AMD provides competitive pricing, delivering good value for gaming enthusiasts across its lineup.
Ultimately, the choice between AMD and Intel for gaming hinges on individual requirements, preferences, and budget constraints.
AMD’s Ryzen 9 5900X and Ryzen 5 5600X provide compelling alternatives, excelling in multi-core performance and offering competitive gaming performance.
The choice between the two hinges on factors such as specific game optimizations and user preferences.
Read More: India’s First Semiconductor Fab to Begin Production by 2026 – techovedas
AMD vs Intel: Productivity and Performance
Productivity and Workload Handling:
Intel’s Core i9 series shines in productivity tasks, leveraging its x86 hybrid architecture to handle diverse workloads efficiently.
| Aspect | AMD Ryzen CPUs | Intel Alder Lake CPUs |
|---|---|---|
| Productivity Performance | Competent, with Ryzen 9 series offering strong multi-threaded performance | Robust, particularly with Intel Core i9 series for diverse workloads |
| Workload Handling | Efficient, with Ryzen CPUs demonstrating versatility across tasks | Highly capable, leveraging hybrid architecture for optimized workload management |
| Single-threaded Performance | Competitive, though not always on par with Intel counterparts | Superior, with Intel CPUs excelling in single-threaded tasks |
| Multi-threaded Performance | Strong, with Ryzen CPUs boasting high core counts and efficient multi-threading | Impressive, especially with Intel’s hybrid architecture optimizing multi-threaded workloads |
| Productivity Features | Offers features like Precision Boost Overdrive and Smart Access Memory | Incorporates technologies like Intel Thread Director for efficient workload distribution |
| Software Optimization | Continues to improve compatibility and optimization with various software | Intel’s focus on driver support and software updates enhances overall performance |
This comparison provides a snapshot of how AMD Ryzen CPUs and Intel Alder Lake CPUs perform in terms of productivity and performance.
Keep in mind that specific models may vary in their capabilities and performance metrics.
AMD vs Intel: Processor Specification and Features
Specifications and Features:
Intel’s offerings often boast lower prices, superior performance, and modern platform support.
| Aspect | AMD Ryzen CPUs | Intel Alder Lake CPUs |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Zen architecture | Alder Lake architecture |
| Manufacturing Process | 7nm technology | Transitioning from 14nm to 10nm technology |
| Core Configuration | Up to 16 cores | Up to 24 cores (including P-cores and E-cores) |
| Thread Support | SMT (Simultaneous Multithreading) | Hyper-Threading (Simultaneous Multithreading) |
| Clock Speed | Up to 5 GHz (Boost Clock) | Up to 5.3 GHz (Boost Clock) |
| Cache Size | Up to 72MB L3 Cache | Up to 30MB L3 Cache |
| Integrated Graphics | AMD Radeon Graphics (select models) | Intel Xe Graphics (select models) |
| Memory Support | DDR4 and DDR5 | DDR4 and DDR5 |
| PCIe Support | PCIe 4.0 and PCIe 5.0 | PCIe 4.0 |
| Overclocking Support | Supported | Supported |
| Thermal Design Power (TDP) | Ranges from 35W to 105W (varies by model) | Ranges from 35W to 125W (varies by model) |
| Platform Compatibility | AM4 socket | LGA 1700 socket |
| Technological Features | Precision Boost Overdrive, Smart Access Memory, Infinity Fabric | Intel Thread Director, Intel Turbo Boost Max Technology 3.0 |
This comparison highlights the key specifications and features of AMD Ryzen CPUs and Intel Alder Lake CPUs, aiding users in making informed decisions based on their specific requirements and preferences.
AMD vs Intel: Power Efficiency
Power Efficiency:
AMD’s utilization of TSMC’s 7nm process grants it an edge in power efficiency and transistor density compared to Intel’s ongoing transition to smaller nodes.
Certainly! Here’s a comparison of AMD and Intel CPUs based on power efficiency in tabular form:
| Aspect | AMD CPUs | Intel CPUs |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Utilizes TSMC’s 7nm technology. | Transitioning from 14nm to 10nm processes, with advancements in “Intel 7” process. |
| Power Consumption | Demonstrates superior power efficiency due to 7nm process. | Improving power efficiency with advancements in manufacturing processes. |
| Thermal Management | Efficient thermal management, resulting in reduced heat generation. | Focus on optimizing thermal performance to minimize heat dissipation. |
| Overall Performance | AMD maintains an edge in power efficiency metrics. | Intel making strides to narrow the gap with advancements in manufacturing. |
This comparison highlights the power efficiency aspect between AMD and Intel CPUs, providing insights into their respective approaches and advancements in managing power consumption and thermal performance.
Although Intel’s advancements with the “Intel 7″ process narrow the gap, AMD maintains superiority in overall power efficiency, resulting in tangible benefits in terms of energy consumption and thermal management.
AMD vs Intel: CPU Architecture
CPU Architecture:
AMD’s Zen 3 architecture and Intel’s Alder Lake architecture represent pinnacle achievements in CPU design, each with distinct strengths and innovations.
While AMD’s focus on efficiency and scalability enhances power consumption metrics, Intel’s hybrid approach introduces new possibilities for performance and versatility, catering to diverse computing needs.
AMD vs Intel: CPU Drivers and Software
Driver Support and Software Optimization:
Both AMD and Intel have made significant strides in improving driver support and software optimization for their CPUs.
| Aspect | AMD CPUs | Intel CPUs |
|---|---|---|
| Driver Support | AMD has made significant improvements in driver updates, ensuring timely support with the latest software. | Intel has focused on enhancing driver updates, particularly for integrated graphics support. |
| Software Optimization | AMD continues to work on optimizing its new architectures for diverse software environments, ensuring seamless performance. | Intel has made strides in improving software optimization, ensuring compatibility and performance across various applications. |
This comparison provides a brief overview of the state of CPU drivers and software support for both AMD and Intel processors.
Intel’s focus on integrated graphics support and timely updates complements AMD’s efforts to optimize its new architectures for diverse software environments, ensuring users experience seamless performance across various applications.
AMD vs Intel: Security
Security Considerations:
In terms of security, AMD CPUs have demonstrated resilience against vulnerabilities like Spectre and Meltdown compared to Intel counterparts.
Certainly! Here’s a comparison of AMD and Intel CPUs in terms of security in tabular form:
| Aspect | AMD CPUs | Intel CPUs |
|---|---|---|
| Vulnerability | Demonstrated resilience against vulnerabilities like Spectre and Meltdown. | Vulnerable to vulnerabilities like Spectre and Meltdown, with varying degrees of mitigation through software patches. |
| Security Updates | Regular security updates are provided to address potential vulnerabilities and ensure system integrity and user safety. | Intel also provides timely security updates to mitigate vulnerabilities and enhance system security. |
| Mitigation | AMD CPUs incorporate mitigation techniques to address security vulnerabilities, prioritizing user data protection. | Intel implements mitigation strategies through software patches to minimize the impact of security vulnerabilities. |
| Focus | AMD prioritizes robust security features to safeguard user data and system integrity, actively addressing emerging threats. | Intel also emphasizes security, working to bolster defenses against potential exploits and vulnerabilities. |
This comparison provides an overview of how AMD and Intel CPUs address security concerns and work to ensure the safety and integrity of user systems.
However, both companies remain vigilant in addressing security concerns through timely software patches and updates, prioritizing user safety and data integrity.
Read More:3 Sectors & 174 Companies Set to Soar as Next Phases of AI Boom as Per Goldman Sachs – techovedas
AMD vs Intel: Desktop Processors
Desktop CPU Options:
AMD and Intel offer a plethora of desktop processors catering to diverse performance requirements and budget constraints.
Certainly! Here’s a comparison of AMD and Intel CPUs in terms of security in tabular form:
| Aspect | AMD CPUs | Intel CPUs |
|---|---|---|
| Vulnerability | Demonstrated resilience against vulnerabilities like Spectre and Meltdown. | Vulnerable to vulnerabilities like Spectre and Meltdown, with varying degrees of mitigation through software patches. |
| Security Updates | Regular security updates are provided to address potential vulnerabilities and ensure system integrity and user safety. | Intel also provides timely security updates to mitigate vulnerabilities and enhance system security. |
| Mitigation | AMD CPUs incorporate mitigation techniques to address security vulnerabilities, prioritizing user data protection. | Intel implements mitigation strategies through software patches to minimize the impact of security vulnerabilities. |
| Focus | AMD prioritizes robust security features to safeguard user data and system integrity, actively addressing emerging threats. | Intel also emphasizes security, working to bolster defenses against potential exploits and vulnerabilities. |
This comparison provides an overview of how AMD and Intel CPUs address security concerns and work to ensure the safety and integrity of user systems.
While Intel’s Core i9-12900KS excels in productivity and gaming, AMD’s Ryzen lineup provides competitive alternatives, with a wide array of offerings tailored to different user preferences and usage scenarios.
AMD vs Intel: Laptop Processors
Laptop CPU Landscape:
Intel’s 12th Gen CPUs dominate the laptop CPU market, offering varying levels of performance across different segments.
Here’s a comparison of AMD and Intel laptop processors in tabular form:
| Aspect | AMD Laptop Processors | Intel Laptop Processors |
|---|---|---|
| Market Dominance | AMD Ryzen Mobile processors have gained significant traction, offering competitive performance and power efficiency in the laptop market. | Intel’s 12th Gen CPUs dominate the laptop CPU market, providing varying levels of performance across different segments. |
| Performance | AMD Ryzen Mobile processors deliver impressive performance, particularly in multi-threaded tasks, providing excellent value for productivity users. | Intel’s laptop CPUs offer varying levels of performance, with options catering to different usage scenarios and performance requirements. |
| Power Efficiency | AMD’s Ryzen Mobile processors are known for their power efficiency, offering longer battery life and improved thermal management in laptops. | Intel’s 12th Gen CPUs strive to balance performance and power efficiency, optimizing battery life and thermal performance for mobile computing. |
| Integrated Graphics | AMD’s Ryzen Mobile processors come with Radeon integrated graphics, offering capable performance for casual gaming and multimedia tasks. | Intel’s integrated graphics solutions provide varying levels of performance, catering to users who require graphics capabilities without discrete GPUs. |
| Platform Support | AMD’s Ryzen Mobile processors are compatible with a range of laptop platforms, offering flexibility for laptop manufacturers and users. | Intel’s laptop CPUs are widely supported across various laptop platforms, ensuring broad compatibility and availability in the market. |
This comparison highlights the key differences between AMD and Intel laptop processors, covering aspects such as performance, power efficiency, integrated graphics, and platform support, helping users make informed decisions based on their specific needs and preferences.
AMD’s offerings also provide compelling alternatives, with considerations extending beyond raw power to factors such as power efficiency and integrated graphics capabilities.
Both companies cater to the diverse needs of laptop users, ensuring a rich ecosystem of options for mobile computing.
Conclusion:
In the perennial debate of AMD vs Intel, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer to which CPU reigns supreme in 2024.
The choice ultimately boils down to individual requirements, preferences, and budget constraints.
Both AMD and Intel continue to push the envelope of CPU technology, ensuring consumers have access to cutting-edge solutions tailored to their unique needs. Whether prioritizing gaming performance,
productivity, power efficiency, or specific features, the diverse offerings from both companies ensure there’s something for everyone in the ever-evolving landscape of computing.



