Introduction
Nvidia has once again taken the lead in the AI infrastructure space with the introduction of the Blackwell GPU architecture during CEO Jensen Huang’s GTC keynote.
This highly anticipated unveiling marks Nvidia’s commitment to extending its technical superiority in both performance and power consumption.
The Blackwell GPUs are set to revolutionize the industry, offering remarkable advancements in performance, power efficiency, and scalability.
As of now, the Blackwell architecture consists of three components: the B100, B200, and the Grace-Blackwell Superchip (GB200).
It is well known that the devil is in the details so let’s decode the release of Nvidia’s Blackwell architecture.
Follow us on Linkedin for everything around Semiconductors & AI
1. Architecture decoded
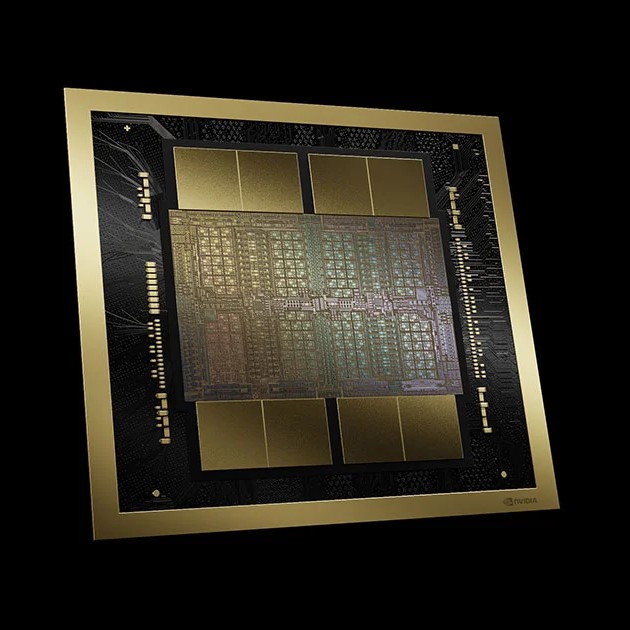
Nvidia’s Blackwell GPU die
Packed with 208 billion transistors, Blackwell-architecture GPUs are manufactured using a custom-built 4NP TSMC process.
Each GPU (B100 & B200) is actually two reticle-limited compute dies, tied together via a 10TB/sec NVLink-HBI (high-bandwidth interface) fabric, which allows them to function as a single accelerator.
The two compute dies are flanked by a total of eight HBM3e memory stacks, with up to 192GB of capacity and 8TB/sec of bandwidth.
And unlike H100 and H200, we’re told the B100 and B200 have the same memory and GPU bandwidth.
Read more How NVIDIA GPUs have Evolved From Tesla to Ampere to Hopper – techovedas
2. Nvidia’s Grace-Blackwell Superchip
Nvidia’s most powerful GPUs can be found in its GB200. Similar to Grace-Hopper, the Grace-Blackwell Superchip meshes together its existing 72-core Grace CPU with its Blackwell GPUs, using the NVLink-C2C interconnect.
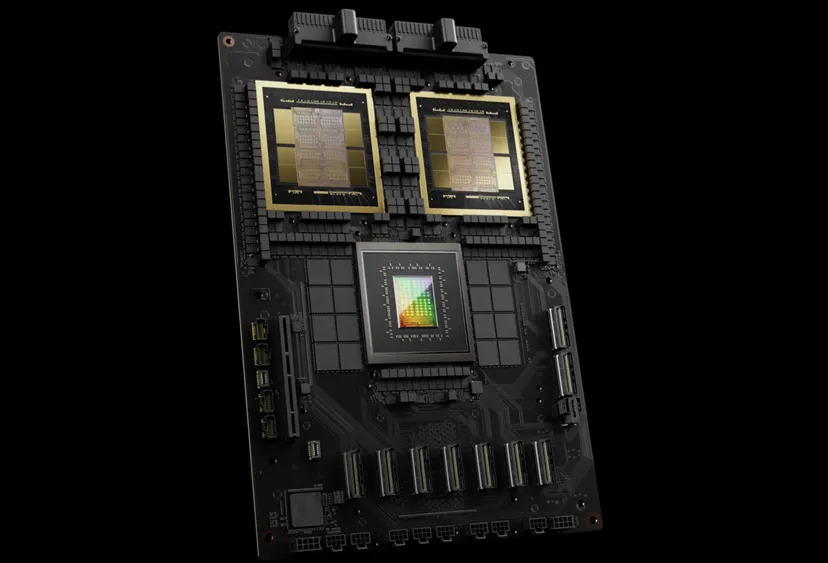

3. Two GPUs, one CPU, one board
But rather than a single H100 GPU, the GB200, integrates a 72-core Grace CPU with a pair of 1,200W Blackwell GPUs of 40 petaFLOPS of FP4 performance each. Thus, the dual GB200 system delivers 80 petaFLOPS of FP4, or 40 petaFLOPS at FP8, while occupying significantly less space.
FP4 refers to the 4-bit floating point data type, a method used by computers to perform calculations. It enables precise representation of numbers, allowing upto 4 decimal places after decimal point.
4. Performance gains
In a strategic move reminiscent of AMD’s MI300-series accelerators. Intel’s GPU Max parts, Nvidia has adopted a chiplet approach to maximise performance gains.
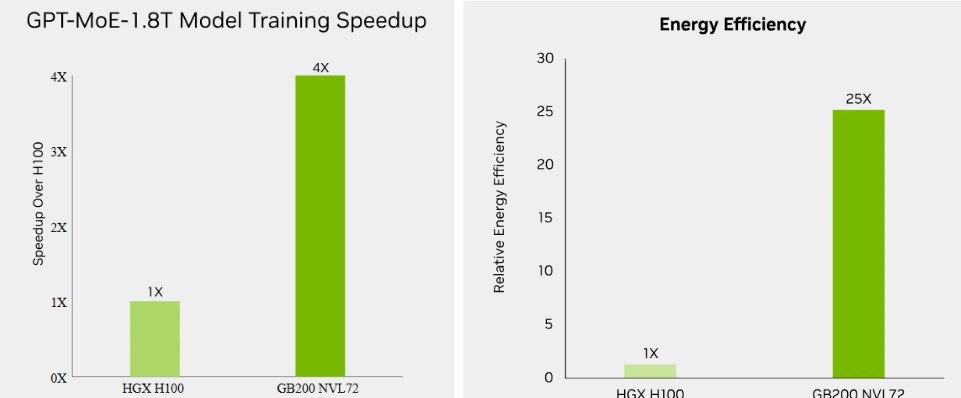
The GB200 NVL72 provides up to a 4x performance increase compared to the same number of NVIDIA H100. Tensor Core GPUs for LLM inference workloads, and reduces cost and energy consumption by up to 25x.
Read more What is So Special about NVIDIA Datacentre GPUs – techovedas
5. Nvidia’s NVL72 rack scale systems
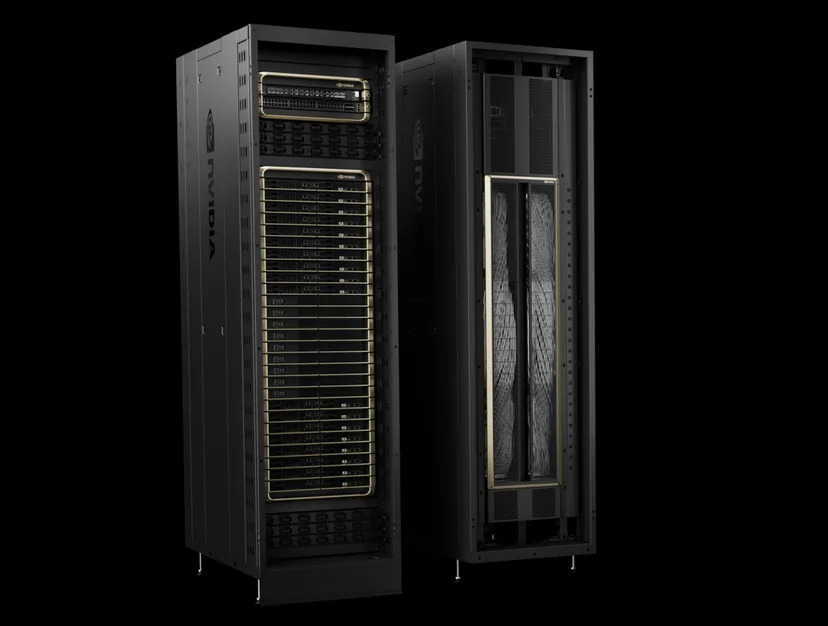

These dual GB200 systems form the backbone of Nvidia’s NVL72 rackscale AI systems, which are designed to support large-scale training . Its inference deployments on models scaling to trillions of parameters.
Each rack comes equipped with 18 nodes, for a total of 32 Grace GPUs and 72 Blackwell accelerators. These nodes are then interconnected via a bank of nine NVLink switches. It is enabling them to behave like a single GPU node with 13.5TB of HBM3e.
Nvidia’s NVLink is a high-speed, energy-efficient interconnect technology that enables ultra-fast communication between CPUs and GPUs or between multiple GPUs
This is actually the same technology employed in Nvidia’s past DGX systems to make eight GPUs behave as one. The difference is that, using dedicated NVLink appliances, Nvidia is able to support many more GPUs.
6. Fifth-Generation NVLink
To accelerate performance for multitrillion-parameter and mixture-of-experts AI models, the latest iteration of NVIDIA NVLink delivers groundbreaking 1.8TB/s bidirectional throughput per GPU. It is ensuring seamless high-speed communication among up to 576 GPUs for the most complex LLMs.
Power Consumption
With the B100, B200, and GB200, the key differentiator comes down to power and performance rather than memory configuration. According to Nvidia, the silicon can actually operate between 700W and 1,200W. It is depending on the Stock keeping unit and type of cooling used.
In order to achieve the full performance, the Blackwell GPU’s thermal demands liquid cooling, facilitating the delivery of the 20 petaFLOPS of FP4.
Read more What is Aritificial Intelligence(AI) Power Problem: A Code Red for Our Planet – techovedas
How Blackwell ranks up so far
While Nvidia may dominate the AI infrastructure market, it’s hardly the only name out there. Heavy hitters like Intel and AMD are rolling out Gaudi and Instinct accelerators, cloud providers are pushing custom silicon, and AI startups like Cerebras and Samba Nova are vying for a slice of the action.
Nvidia Blackwell vs AMD MI300X
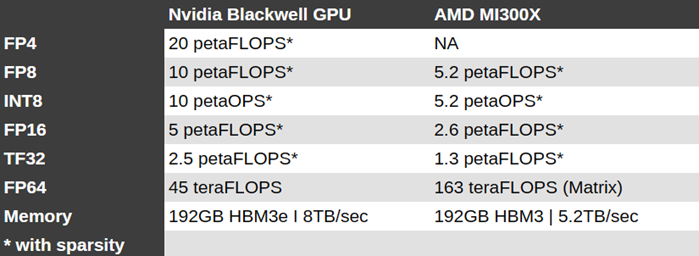
In terms of performance, the MI300X promised a 30 percent performance advantage in FP8 floating point calculations and a nearly 2.5x lead in HPC-centric double precision workloads compared to Nvidia’s H100.
Comparing the 750W MI300X against the 700W B100, Nvidia’s chip is 2.67x faster in sparse performance. And while both chips now pack 192GB of high bandwidth memory, the Blackwell part’s memory is 2.8TB/sec faster.
AMD’s Instinct MI300X
Memory bandwidth has already proven to be a major indicator of AI performance, particularly when it comes to inferencing. Nvidia’s H200 is essentially a bandwidth boosted H100. Yet, despite pushing the same FLOPS as the H100, Nvidia claims it’s twice as fast in models like Meta’s Llama 2 70B.
While Nvidia has a clear lead at lower precision, it may have come at the expense of double precision performance – an area where AMD has excelled in recent years, winning multiple high-profile supercomputer awards.
Conclusion
Nvidia’s unveiling of the Blackwell GPU architecture at the GTC keynote signifies a substantial leap in AI infrastructure.
The architecture, embodied in the B100, B200, and the formidable Grace-Blackwell Superchip GB200, offers unparalleled scalability through innovative design and technology.
The NVL72 rackscale AI systems, powered by Blackwell accelerators and NVLink switches, enable large-scale training and inference deployments, further cementing Nvidia’s dominance in the AI infrastructure market.
As competition intensifies, particularly with AMD’s MI300X and Cerebras’s WSE-3, Nvidia’s focus on optimization for power and performance sets a new benchmark in the industry, ensuring its leading position in the evolving landscape of AI infrastructure.




