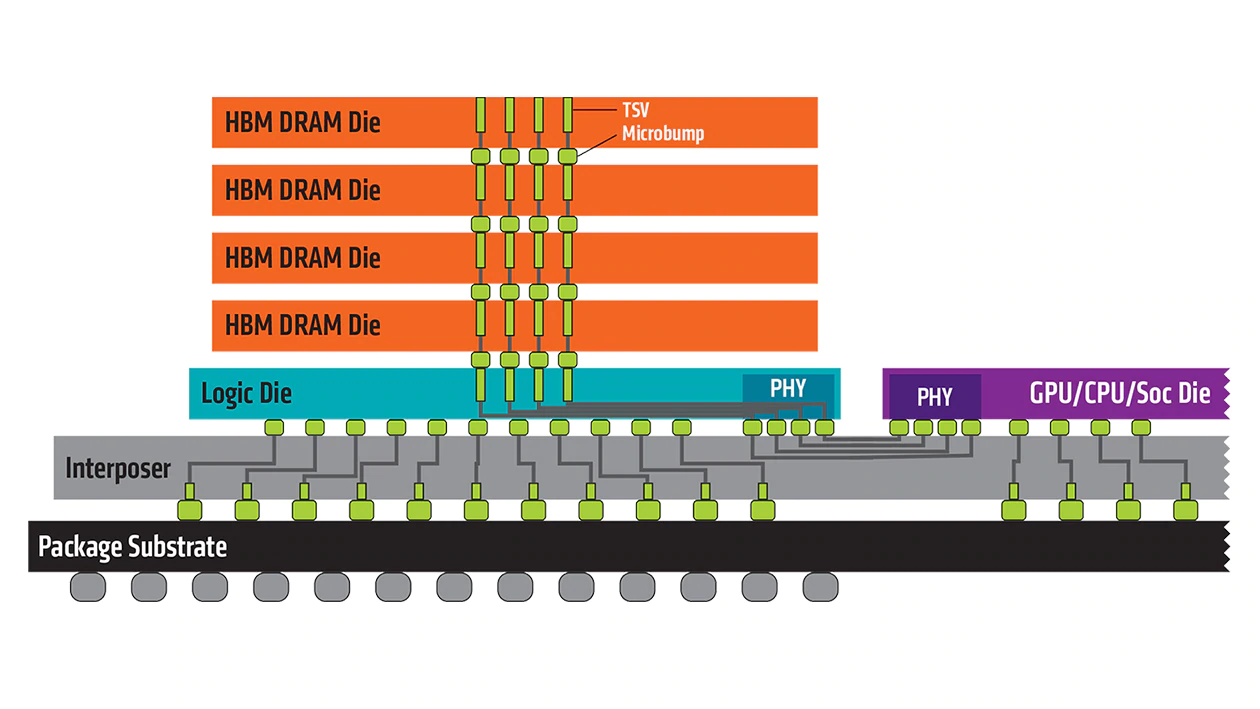
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of computer technology, memory plays a pivotal role in determining the overall performance of a system. As demands for faster and more efficient data processing continue to rise, innovative solutions like High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) have emerged to address the challenges posed by traditional memory architectures.
In this blog post, we will explore the significance of HBM, its applications, and how it stands out from current memory technologies.
Why Do We Need HBM?
1. Data-Hungry Workloads:
In today’s computing environment, applications demand unprecedented levels of data processing. Whether it’s rendering lifelike graphics in gaming or performing complex simulations in scientific research, the need for high-speed access to vast amounts of data is evident. HBM’s primary purpose is to meet these demands by providing exceptionally high bandwidth, ensuring that data can be swiftly moved between the processor and memory.
2. Graphics Intensity:
Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) have become the workhorses for rendering realistic visuals in gaming, 3D modeling, and professional graphics work. These applications require immense computational power and rapid access to graphical data. HBM, with its superior bandwidth, is tailor-made for these graphics-intensive workloads, enabling a smoother and more immersive user experience.
3. High-Performance Computing (HPC):
Beyond gaming and graphics, HBM finds applications in High-Performance Computing (HPC) scenarios. Scientific simulations, weather forecasting, and other data-intensive computations demand memory solutions that can keep up with the processing power of modern CPUs and GPUs. HBM’s ability to deliver high bandwidth makes it well-suited for these HPC applications.
Read More: What is Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)and Why Should You Care? – techovedas
Contrasting HBM with Current Memory Technologies
1. Traditional Memory (e.g., GDDR):
Traditional memory technologies, such as GDDR (Graphics Double Data Rate) memory, have served well in the past. However, they face limitations in terms of bandwidth and power efficiency. HBM’s stacked design and wide bus interface offer a significant contrast, providing higher bandwidth and reduced power consumption.
2. Stacked Architecture:
HBM’s stacked architecture sets it apart from traditional memory. By stacking multiple memory dies vertically, HBM reduces latency and shortens communication paths, resulting in faster data transfer rates. In contrast, traditional memory modules are arranged side by side on a flat surface.
3. Wide Bus Interface:
The wide bus interface of HBM enables parallel data transmission, allowing for more data to be transferred simultaneously. This is in contrast to the narrower interfaces found in traditional memory technologies, which can limit the speed at which data can be exchanged.
4. Energy Efficiency:
HBM’s energy-efficient design is a significant advantage over some traditional memory architectures. The stacked design and reduced power consumption make HBM a compelling choice for devices with power constraints, offering a balance between performance and energy efficiency.
Major Applications of HBM
1. Gaming and Graphics:
HBM has found a natural home in gaming GPUs. The seamless flow of graphical data enabled by HBM contributes to more realistic visuals, smoother frame rates, and an overall improved gaming experience.
2. Professional Graphics Work:
Professionals working in fields like graphic design, video editing, and 3D modeling rely on GPUs with high memory bandwidth to handle large datasets efficiently. HBM enhances the performance of these applications, allowing for quicker rendering and smoother workflows.
3. High-Performance Computing (HPC):
Scientific simulations and calculations in HPC require massive computational power and rapid data access. HBM’s high bandwidth facilitates the quick exchange of data, making it a crucial component in supercomputers and research clusters.
Read More: What is Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) : Possibilities & Danger – techovedas
Conclusion
In conclusion, High Bandwidth Memory emerges as a crucial innovation in the realm of computer memory, addressing the escalating demands of modern applications. Its applications in gaming, professional graphics work, and high-performance computing underscore its versatility and impact. As technology continues to advance, HBM stands as a testament to the ongoing pursuit of faster, more efficient, and more powerful computing solutions.