Introduction
TSMC recently revealed its ambitious technology roadmap at the International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 2023 conference. The roadmap outlines TSMC’s Roadmap plans for driving innovations in cutting-edge semiconductor manufacturing processes and advanced 3D packaging over the next decade. Additionally, TSMC aims to push beyond current process limitations to enable new generations of high-performance computing applications.
Join TechoVedas Community here
7 Pillars of TSMC Roadmap to Chip Supremacy by 2030
1. Advancing Leading-Edge Process Nodes
TSMC remains on schedule for introducing its next-gen N2 and N2P nodes between 2025-2027, which will utilize FinFET transistor architectures
Longer-term, TSMC is gearing up for 1nm gate-all-around nanosheet transistor technology (A10 node) and 1.4nm (A14 node) targeted for 2027 to 2030.
These process advancements follow Moore’s Law and deliver benefits like increased transistor density and power efficiency.
Read More: TSMC to Build 1nm Transistors by 2030
2. Accelerating Transition to 3D Chiplet Integration
TSMC is aggressively developing 3D packaging solutions for integrating multiple chiplets in vertical configuration.
Company forecasts crossing 1 trillion transistors for 3D heterogeneous systems as early as 2030.
Modular 3D chiplet approach provides flexibility, yield, and cost benefits over conventional large monolithic dies.
Read More: 4 Major Takeaways from TSMC Chairman Mark Liu’s Retirement
3. Pushing Boundaries of Monolithic Chip Complexity
Monolithic chips are crucial for achieving the highest density in semiconductor technology, and additionally,TSMC’s roadmap indicates a projection of nearly 200 billion transistors on monolithic chips by 2030. 
For context, the NVIDIA H100 GPU fabricated by TSMC incorporates 108 billion transistors on a monolithic die, showcasing the significant leap in transistor count envisioned by TSMC over the next decade.
Read More: How Well Do You Know TSMC? Take Our Quiz to Find Out! – techovedas
4. Additional Technological Progress:
TSMC plans to commence risk production of 2nm gate-all-around nanosheet transistor technology around 2026, indicating a significant leap towards greater miniaturization and enhanced performance.
Furthermore, TSMC is evaluating multiple technology options as potential candidates for the sub-1nm regime, reflecting their commitment to continuous innovation and pushing the limits of semiconductor capabilities.
Additionally, TSMC is focused on further scaling down the size of SRAM cells, aiming for sizes approaching less than 0.02 μm, which promises improved efficiency and integration in future semiconductor designs.
Read More: What are Emerging Transistor Technologies: Nanosheets & Nanowires
5. Overcoming Key Roadblocks
TSMC is addressing placement congestion challenges through the development of fin depopulation strategies. This aims to optimize the allocation of components on the chip to overcome layout limitations.
Additionally, TSMC is focused on refining nanosheet widths and shapes to minimize access resistances, as well as incorporating novel low-resistance (low-R) materials to mitigate parasitic resistance, signifying their commitment to addressing performance constraints associated with advanced semiconductor technologies.
Read More: Intel Breakthrough Industry First 3D Stack CMOS takes Moore’s law to New Heights
6. Broadening Focus on Interconnects
The incorporation of Cu hybrid bonding utilizes both metal and dielectric bonding surfaces. This reflects TSMC’s interest in advancing interconnect technologies for enhanced performance and efficiency. 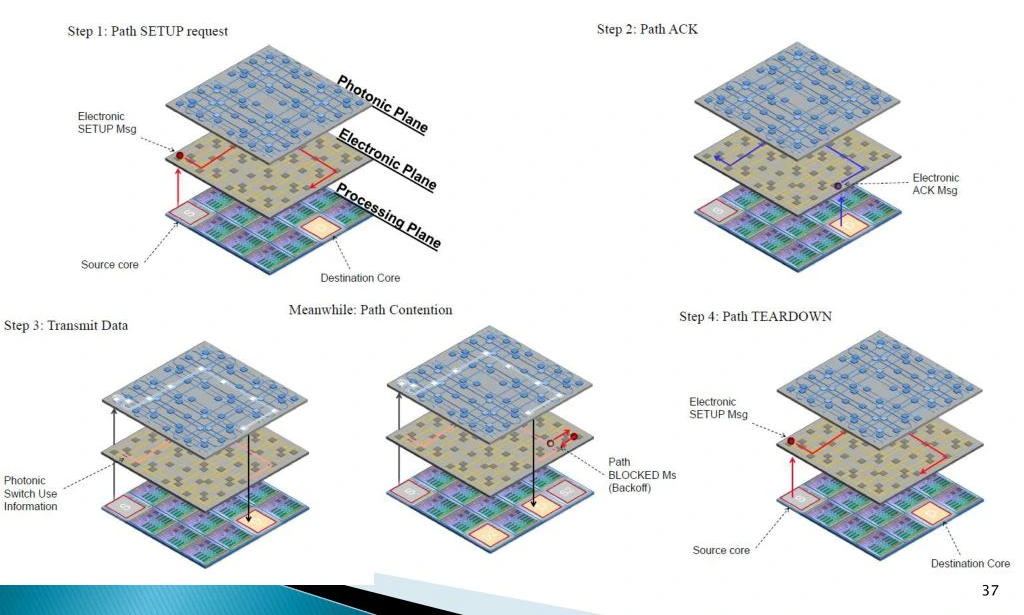
TSMC is investigating low-resistance (low-R) inter-tier vias for 3D stacked architectures, aiming to enhance interconnect efficiency and overall performance. TSMC is actively researching photonics interconnects as a means of improving chiplet links. This suggests a potential shift towards light-based communication for enhanced chiplet interconnections.
Read More: TSMC to Build 1nm Transistors by 2030 – techovedas
7. Balancing Trade-Offs
Additonally,Recognizing that modular solutions outpace monolithic chips in complexity growth, TSMC remains dedicated to advancing transistor-level innovations to maximize density and efficiency.
TSMC strategically balances technological advancements with practical applications in high-demand sectors, primarily limiting the adoption of monolithic solutions to the most demanding High-Performance Computing (HPC) applications.
Read more: What is Heterogeneous integration: Advantages Types and Technology
Conclusion
With its detailed technology roadmap spanning advanced manufacturing processes and 3D integration innovations over the next decade, TSMC seeks to strengthen its industry leadership. Additionally, The company’s projections reveal its confidence in being able to push boundaries and execute on delivering transformative solutions to fuel the world’s rising demands for high-performance computing power across a range of applications. Additionally, If realized, these technologies promise to be the foundational enablers spurring future waves of innovation.