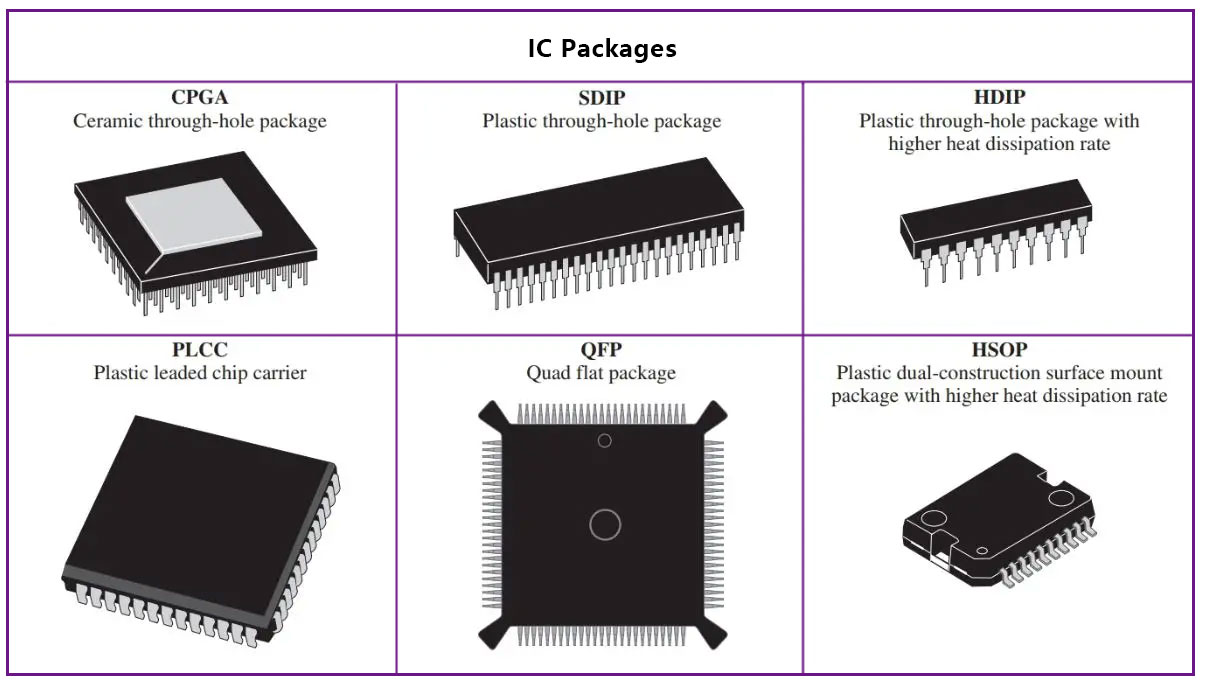
Introduction:
Semiconductor chips are the building blocks of modern electronic devices In the semiconductor industry, chips serve as the backbone, driving a myriad of electronic products, from smartphones and laptops to cars and medical equipment. However, before integrating these chips into electronic products, they require protective packages to facilitate their connection to circuit boards. In this beginner’s guide, we’ll delve into the 5 different types of chip packages commonly employed in the semiconductor industry.
We’ll discuss their respective advantages and disadvantages, as well as their common applications.
Follow us on LinkedIn for everything around Semiconductors & AI
1. Dual In-Line Package (DIP):
- Description: DIP packages feature two parallel rows of pins along the sides of the package.
- Advantages: DIP packages are easy to handle and solder onto circuit boards, making them suitable for through-hole assembly.
- Disadvantages: DIP packages take up more space on circuit boards and may have limitations in pin count and thermal performance.
- Common Applications: DIP packages are commonly used in applications such as industrial control systems, legacy electronic equipment, and hobbyist projects.
Read More:AI GPU Market 2024: NVIDIA dominates with $40B, AMD rises to $3.5B, Intel lags at $500M – techovedas
2. Quad Flat Package (QFP):
- Description: QFP packages have pins arranged in a grid pattern on all four sides of the package.
- Advantages: QFP packages offer high pin counts in a small footprint and are easier to manufacture.
- Disadvantages: QFP packages may have thermal dissipation limitations and may not be suitable for high-frequency applications.
- Common Applications: QFP packages are commonly used in consumer electronics, including televisions, gaming consoles, and home appliances.
Read More: NVIDIA Crowns OpenAI King of AI with World’s First DGX H200 – techovedas
3. Ball Grid Array (BGA):
- Description: BGA packages feature solder balls arranged in a grid pattern on the bottom of the package.
- Advantages: BGAs offer high pin counts and excellent thermal performance, suitable for surface mount assembly.
- Disadvantages: BGAs may be challenging to inspect and repair and require specialized equipment for rework.
- Common Applications: BGA packages are commonly used in computer motherboards, networking equipment, and automotive electronics.
Read More: 4 Talks on Future of Semiconductor Industry by Intel Nvidia AMD and TSMC CEO – techovedas
4. Small Outline Integrated Circuit (SOIC):
- Description: SOIC packages have pins arranged in a single or dual row along the sides of the package.
- Advantages: SOIC packages offer a good balance of pin count, size, and ease of assembly.
- Disadvantages: SOIC packages may have limitations in pin count and thermal performance compared to other package types.
- Common Applications: SOIC packages are commonly used in industrial automation, telecommunications equipment, and medical devices.
5. Quad Flat No-Lead (QFN):
- Description: QFN packages have exposed pads on the bottom instead of leads.
- Advantages: QFN packages offer a compact footprint, excellent thermal performance, and good electrical performance at high frequencies.
- Disadvantages: QFN packages may be challenging to solder and inspect, requiring careful attention to soldering parameters.
- Common Applications: QFN packages are commonly used in mobile phones, tablets, wireless routers, and other portable electronic devices.
Comparison
| Chip Package | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Dual In-Line Package (DIP) | – Widely used and cost-effective. – Ease of assembly and repair. – Good electrical performance. | – Larger footprint on PCBs. – Limited thermal dissipation. – Not suitable for miniaturized designs. |
| Ball Grid Array (BGA) | – Superior thermal performance and reliability. – Smaller footprint on PCBs. – Simplified manufacturing processes. | – Rework and repair challenges. – Higher manufacturing costs. – Limited accessibility for testing. |
| Quad Flat Package (QFP) | – Balance between performance, size, and cost. – Better electrical performance and thermal dissipation than DIP. | – Larger footprint compared to modern packages. – Limited suitability for high-frequency applications. – Additional space requirements on PCBs. |
| Chip-Scale Package (CSP) | – Smallest footprint among traditional packages. – Excellent electrical performance and thermal dissipation. | – Specialized assembly and handling requirements. – Limited accessibility for testing. – Susceptibility to mechanical stress. |
| System in Package (SiP) | – Integration of multiple chips/components into a single package. – Heterogeneous integration for custom applications. – Flexibility in design. | – Complex design and manufacturing processes. – Higher development costs. – Thermal and signal integrity challenges. |
Read More: 5 Step Method To Build Your First Electronic Gadget With Arduino – techovedas
Conclusion:
Choosing the right semiconductor chip package is essential for optimizing the performance, reliability, and manufacturability of electronic devices.
Each package type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making it crucial for designers and engineers to consider their specific application requirements when selecting the most appropriate package.