Introduction
Humanoid robots, once confined to the realm of science fiction, are now on the cusp of revolutionizing the workplace. These bipedal machines, capable of performing a multitude of tasks, have captured the imagination of scientists, engineers, and sci-fi enthusiasts alike. However, the journey from concept to commercial reality has been fraught with challenges. Despite significant investments and advancements in technology, the road to widespread adoption of humanoid robots in the workplace has been anything but straightforward.
What are humanoid robots?
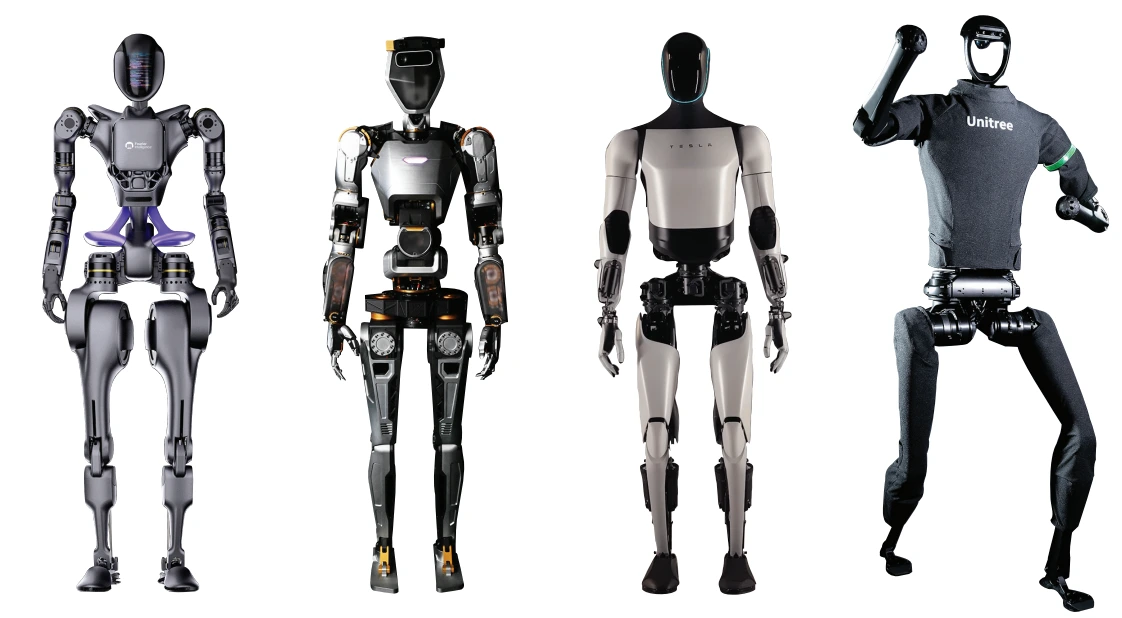
A humanoid robot can be defined as the programmable machine which can imitate the tasks of humans as well as their appearance. Humanoid research helps researchers to understand more about human structure and behaviour.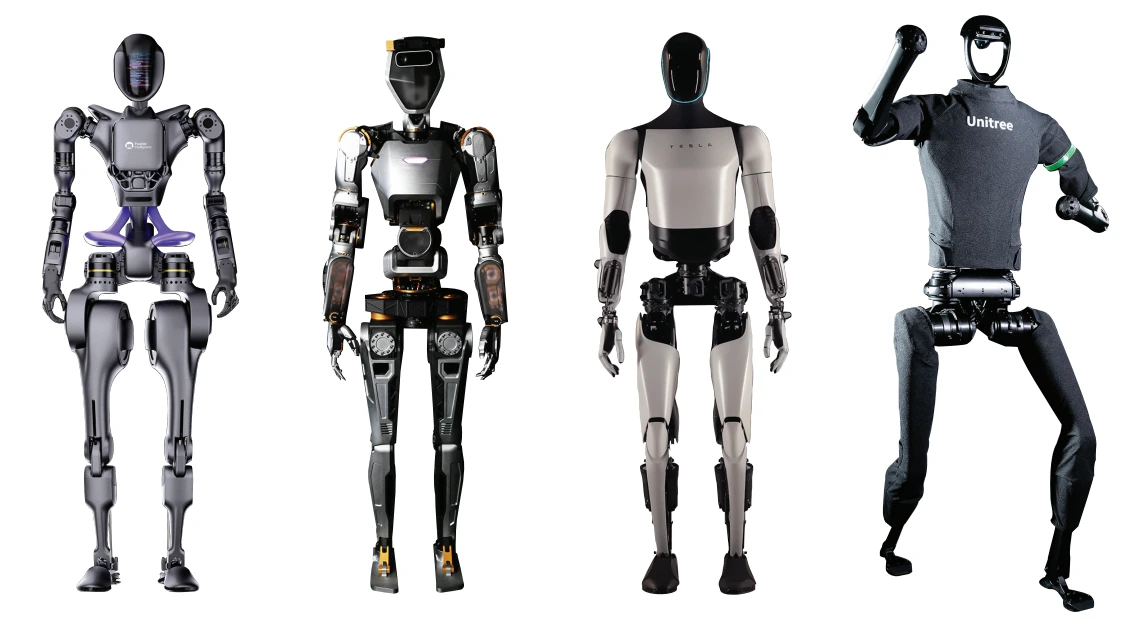
After years of research and development in this field, humanoids are now available in different shapes, sizes, and capabilities based on their application area. Most of the humanoid comes with one torso, two legs, two hands, and head. But in some applications, partial body parts are designed to perform specific work or research, such as only the lower part of the body to perform research operations on the gait of the robot.
Read More: How Baidu and Lenovo are Shaping the Future of AI Smartphones in China – techovedas
Advancements in Humanoid Robotics
One of the key areas of advancement in humanoid robotics is in the development of robust software algorithms. These algorithms are essential for enabling robots to perform tasks with precision and efficiency, while also ensuring safety and reliability.
Machine learning and artificial intelligence techniques are increasingly being utilized to enhance robot intelligence and adaptability, enabling them to learn from experience and improve their performance over time.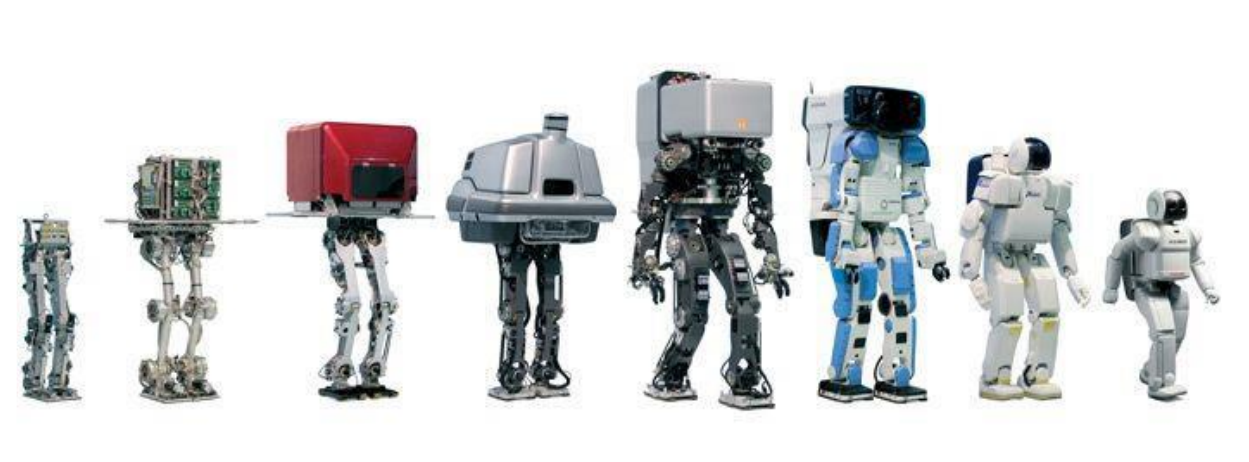 
As a result, humanoid robots are becoming increasingly capable of autonomously carrying out a wide range of tasks, from simple manipulation to more complex decision-making and problem-solving.
Additionally, advancements in materials science and manufacturing technologies have led to the development of lighter, stronger, and more durable materials for constructing humanoid robots. This has resulted in robots that are not only more capable but also more energy-efficient and cost-effective to produce.
Challenges in making humanoid robots
Despite progress, significant challenges persist in the development and deployment of humanoid robots. From the complexities of actuator technology to the limitations of current battery systems, technological hurdles must be overcome to realize the full potential of these machines in the workplace.
By the way an actuator is a component of a machine that produces force, torque, or displacement when an input impulse is supplied to it.
This was hardware. On the software side development of robotics presents several unique challenges that engineers and researchers must overcome to create intelligent and capable machines. Some of the key challenges include:
1.Complexity and Variability: Robotics software must be able to handle the complexity and variability of real-world environments. This includes dealing with unpredictable events, such as changes in lighting conditions, variations in terrain, and unexpected obstacles.
2.Sensor Fusion: Robots rely on various sensors, including cameras, lidar, and depth sensors, to perceive their surroundings. Integrating data from multiple sensors and fusing it into a coherent representation of the environment is a complex task that requires sophisticated algorithms.
3.Motion Planning: Planning the motion of a robot in real-time while avoiding collisions with obstacles is a challenging problem. Motion planning algorithms must be able to generate safe and efficient trajectories that account for the robot’s kinematics and dynamic constraints.
Moreover, issues such as manufacturability, supply chain resilience, and service infrastructure pose additional obstacles on the path to commercial success.
Competing in a Crowded Market
Agility Robotics is not alone in its pursuit of commercializing humanoid robots. Several other companies, including Apptronik, 1X Technologies, Figure, Fourier Intelligence, Sanctuary AI, Tesla, and Unitree, are investing heavily in this burgeoning field.
With substantial funding and ambitious prototypes, competition is fierce as companies vie for dominance in the market. Collaboration and innovation are key as these companies navigate the complexities of bringing humanoid robots to the forefront of automation.
Robots to Lookor in 2024
Singapore-based Fourier Intelligence is already massproducing its GR-1 robot. Fourier’s background is in healthcare robotics, and the company sees potential applications for GR-1 in medical and rehabilitation contexts, although the robot will also be available to researchers seeking a humanoid development platform.
Read More: 5 FREE Courses on AI and ChatGPT to Take You From 0-100 – techovedas
SANCTUARY AI: PHOENIX
Sanctuary AI’s goal is to “create the world’s first humanlike intelligence in general-purpose robots.” To accomplish this, the company has been collecting extensive amounts of data of humans teleoperating its robots through complex manipulation tasks. Sanctuary AI hopes to leverage that data to train its robots to perform those tasks autonomously.
TESLA: OPTIMUS
Tesla has some unique advantages when it comes to building and deploying robots. The company has substantial experience in battery technology, as well as in sensing and computing for mobile systems. And Tesla is potentially its own first customer for humanoids, finding work for them in its car factories.
UNITREE ROBOTICS: H1
Unitree, a Chinese company established in 2016, is famous for producing affordable quadrupedal robots. Their debut humanoid robot, priced under $90,000, serves as an economical hardware base for robotics research or software-centric companies.
Conclusion
As the year of the humanoid dawns, the promise of bipedal robots in the workplace is more tangible than ever before. With companies like Agility Robotics leading the charge and a crowded market of competitors vying for dominance, the stage is set for a transformative shift in how we approach repetitive labour. While challenges remain, the determination and ingenuity of innovators in the field suggest that the age of humanoid robots is not merely a fantasy but a tangible goal within reach. Now, more than ever, the world awaits the arrival of these machines to deliver on their potential and reshape the future of work.