From smartphones and laptops to complex machinery and artificial intelligence systems, semiconductor chips are the unsung heroes behind the scenes.
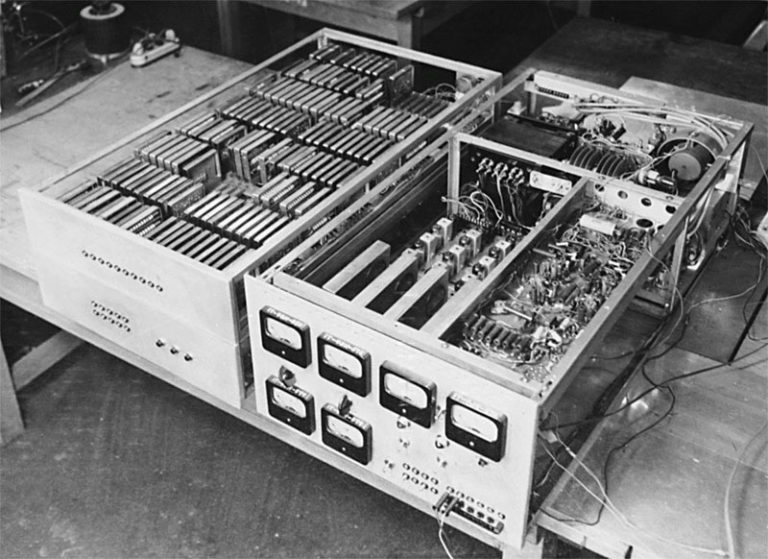
The first digital computers were invented in the 1940s, using vacuum tubes as the basic building blocks. These devices were large, expensive, and unreliable, but they paved the way for the development of the first AI systems

Did you know that training one machine translation model may generate the same amount of CO2 as 36 ordinary Americans in a year?

AI grapples with a significant hurdle – the memory bottleneck, impeding performance and scalability.

The year 2023 witnesses a fierce competition among AI hardware companies, each vying to introduce state-of-the-art products that redefine the benchmarks of power, efficiency, and scalability.
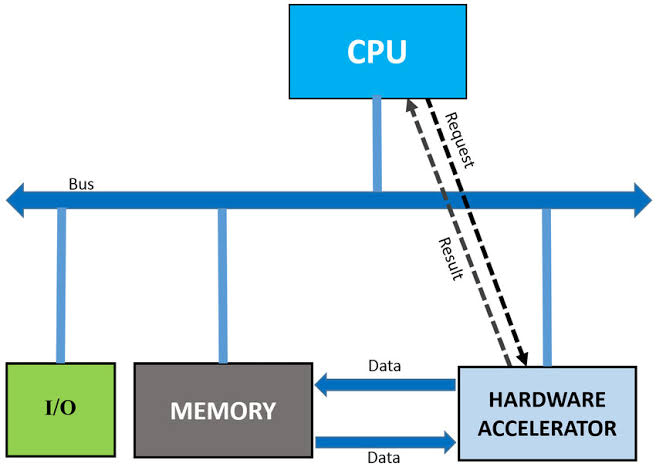
Researchers and engineers, in response to the increasing demand for AI, have been developing a variety of hardware accelerators—specialized devices that can speed up AI workloads and reduce power consumption.
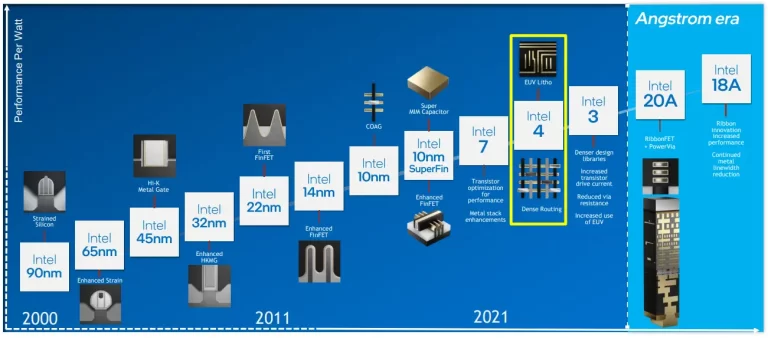
Delve into the intricate stages of Node Evolution, tracing the semiconductor industry's growth from inception to current breakthroughs.
The goal of Parallel Processing is to divide a larger task into smaller subtasks that can be processed independently and concurrently, ultimately speeding up the overall computation.
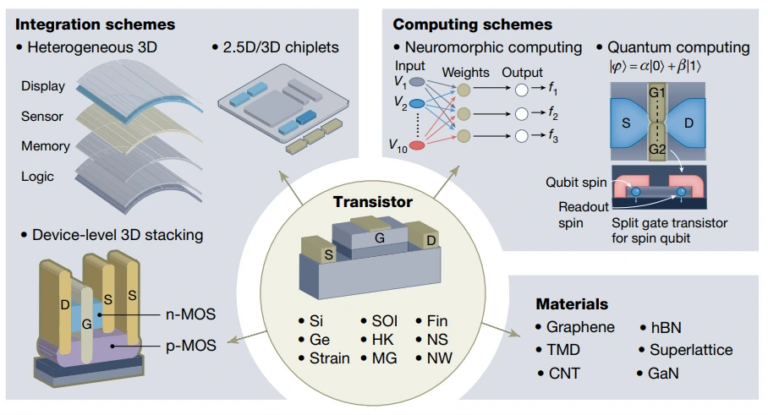
The limitations of MOSFETs in terms of power consumption and energy efficiency have prompted the exploration of ‘beyond MOSFET’ transistors, aiming to break the energy-efficiency bottleneck.

AI algorithms require vast amounts of computational power for training and inference. Hardware AI, such as GPU is optimized for parallel processing, significantly speeding up these computations and making AI tasks more efficient.








