Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become the most transformative force in the global economy, impacting every sector from healthcare to finance. But its journey to ubiquity wasn’t a straight line. This article delves into the five distinct waves of AI computing, tracing its evolution from its early inception to its current frontiers.
Follow us on Linkedin for everything around Semiconductors & AI
The Big Bang of AI: The Birth of Deep Learning
The first wave of AI computing was its “big bang”, which started with the discovery of deep neural networks.
This was a breakthrough in machine learning, a branch of AI that enables computers to learn from data and perform tasks that normally require human intelligence.
Deep neural networks are inspired by the structure and function of the human brain, consisting of layers of interconnected nodes that process information and learn from feedback. 
By feeding these networks millions of examples of inputs and outputs, such as images and labels, researchers were able to train them to perform complex tasks, such as recognizing faces, translating languages, and playing games.
Three factors fueled the big bang of AI: academic breakthroughs in deep learning, the widespread availability of big data, and the novel application of GPUs (graphics processing units) to accelerate deep learning development and training. GPUs, specialized chips that perform parallel computations much faster than CPUs (central processing units), proved ideal for handling the massive amounts of data and calculations required by deep learning.
Read More: 7 Major Takeaways from NVIDIA 769% Annual Profit Growth In Q4Y24 Earnings – techovedas
The Cloud: The Rise of AI Services
The first businesses to use AI were large tech companies with the scientific know-how and computing resources to adapt neural networks to benefit their customers.
The cloud is a network of servers that provide on-demand access to computing power, storage, and software over the internet. By using the cloud, tech companies were able to scale up their AI capabilities and offer them as services to users around the world.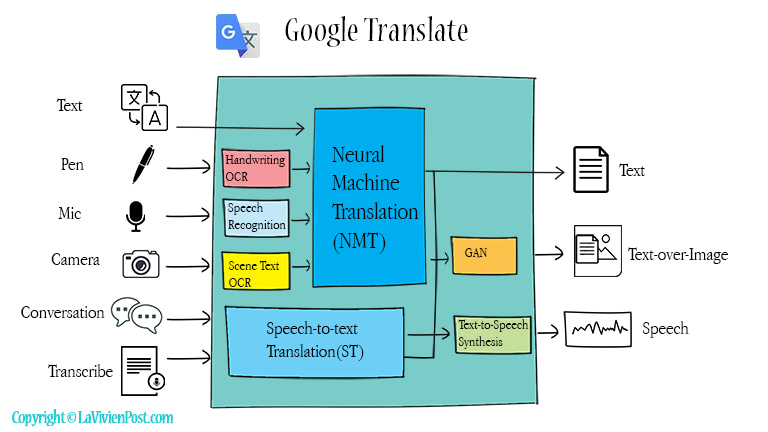
Some of the first and most popular AI services were based on natural language processing (NLP), a subfield of AI that deals with understanding and generating human language. For example, Google applied deep learning to NLP to offer Google Translate, a service that can translate text and speech between over 100 languages. Facebook applied AI to identify consumer goods from images to make them shoppable. Amazon applied AI to recommend products and services to customers based on their preferences and behavior.
Through these types of cloud applications, tech companies introduced many of AI’s first real-world applications, and demonstrated its value and potential to consumers and businesses alike. Soon, these tech companies created infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) platforms, such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, that unleashed the power of public clouds for enterprises and startups alike, and drove AI adoption further.
Read More: What is So Special about NVIDIA Datacentre GPUs
Enterprise AI: The Democratization of AI Solutions
The third wave of AI computing is enterprise AI, which refers to the adoption and integration of AI solutions by businesses across different industries and domains.
Enterprise AI is enabled by the availability and affordability of cloud-based AI services, as well as the development of AI platforms and tools that make AI more accessible and user-friendly. For example, NVIDIA’s Fleet Command is a cloud-native platform that simplifies the deployment and management of AI applications at scale. Microsoft’s Power Platform is a low-code/no-code platform that empowers anyone to build and use AI solutions without coding.
Enterprise AI also leverages domain knowledge and data from various sources, such as sensors, cameras, databases, and social media, to create customized and optimized AI solutions. Salesforce’s Einstein integrates with various CRM (customer relationship management) functions, such as sales, service, and marketing, to enhance customer engagement and satisfaction.
Read More: 5 Top AI Cloud Services You Need to Know in 2024 – techovedas
Edge AI: The Proliferation of AI Devices
The fourth wave of AI computing is edge AI, which refers to the deployment and execution of AI applications on devices that are close to the source of data and the point of action, such as smartphones, cameras, drones, robots, and cars.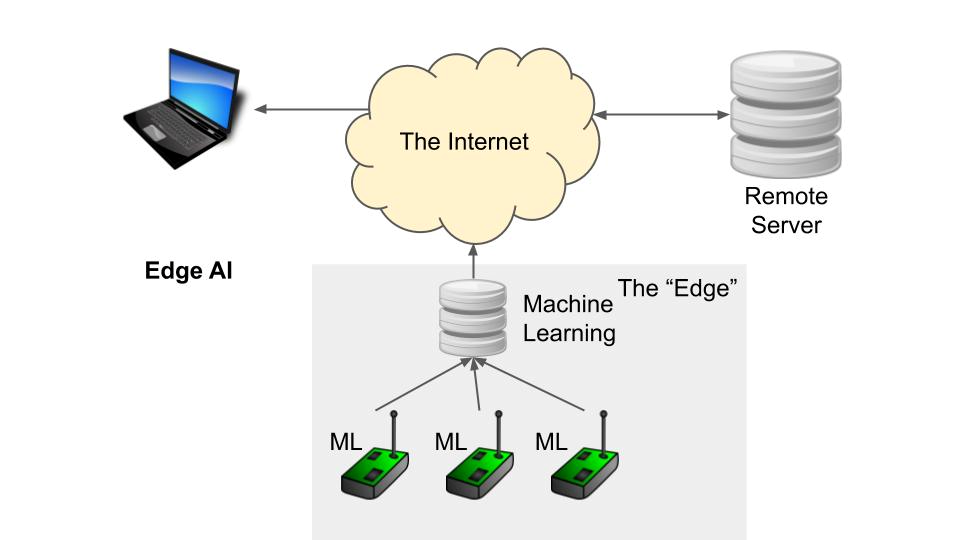
Edge AI is enabled by the advancement and miniaturization of hardware and software technologies, such as edge computing, 5G, IoT (internet of things), and AI chips. Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that processes data at the edge of the network, instead of sending it to the cloud. 5G is a wireless communication technology that offers high-speed, low-latency, and reliable connectivity for edge devices. IoT is a network of physical objects that are embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, that can collect and exchange data. AI chips are specialized chips that can perform AI computations efficiently and effectively on edge devices.
Edge AI offers several benefits and opportunities for users and businesses, such as real-time performance, reduced costs, enhanced security, and improved user experience. For example, edge AI can enable smart home devices, such as cameras, speakers, and thermostats, to respond to user commands and preferences instantly and privately.
Read More: 10 Free AI Tools That Will Blow Your Mind – techovedas
Autonomy: The Future of AI Systems
The fifth and final wave of AI computing is autonomy, which refers to the ability of AI systems to operate and adapt independently, without human intervention or supervision.
The combination and integration of various AI technologies and techniques enable autonomy. These include computer vision, natural language processing, speech recognition, machine learning, deep learning, reinforcement learning, and generative adversarial networks.These technologies and techniques allow AI systems to perceive, understand, communicate, learn, and create, in ways that mimic or surpass human abilities.
Autonomy offers immense possibilities and benefits for humanity, such as enhancing productivity, creativity, innovation, and well-being. For example, Autonomous AI systems can generate new knowledge, products, and services, that can improve the quality of life and solve the world’s biggest problems, such as climate change, poverty, and disease.
Read More:5 Things to know about H100: Chip Behind Nvidia $ 2T Valuation – techovedas
Conclusion
AI computing has evolved over time, from its inception to its ubiquity, through five waves of growth: the big bang of AI, cloud services, enterprise AI, edge AI, and autonomy. Each wave has brought new opportunities and challenges for AI research and applications, and has shaped the world we live in today.
As AI computing continues to advance and innovate, we need to be aware of its history, current state, and future direction, and how it affects us as individuals, businesses, and society. We also need to be proactive and responsible in using and developing AI, to ensure that it serves our needs and goals, and that it creates a positive and sustainable impact for ourselves and others.