Introduction
In recent years, the global semiconductor industry has witnessed a significant shift in power dynamics, particularly concerning American export controls and the emergence of American Export Controls vs. China’s Semiconductor Industry equipment manufacturers.
Amidst escalating trade tensions and geopolitical rivalries, the intricate interplay between technology, market dynamics, and regulatory frameworks has become increasingly apparent.
One of the primary concerns revolves around the utilization of American export controls to influence critical inputs in semiconductor manufacturing, particularly Electronic Design Automation (EDA) tools and capital equipment.
These tools serve as pivotal chokepoints, strategically positioned to regulate access to advanced semiconductor fabrication technologies. Let’s delve deeper into the key aspects of this intricate ecosystem:
Follow us on Linkedin for everything around Semiconductors & AI
1. Electronic Design Automation (EDA) Tools:
The landscape of EDA tools is currently dominated by industry giants such as Cadence, Synopsys, and Siemens/Mentor Graphics.
Despite emerging Chinese competitors, their limited market presence outside of China poses significant structural constraints.
China’s Response: SEIDA
SEIDA: China’s answer to American EDA tool monopoly
China EDA Counterpart, SEIDA’s target is broad, encompassing various EDA tools used throughout the chip design process, including:
- Front-end tools: for design and simulation (e.g., logic synthesis, placement & routing)
- Back-end tools: for physical design and manufacturing (e.g., layout, verification)
- Implementation tools: for translating designs into manufacturing instructions
Read More:A New RISC-V Breakthrough Chip Merges CPU, GPU & AI into One – techovedas
2. Fabrication Equipment:
In the realm of semiconductor fabrication, capital equipment plays a crucial role, particularly in lithography, deposition, etching, and process control.
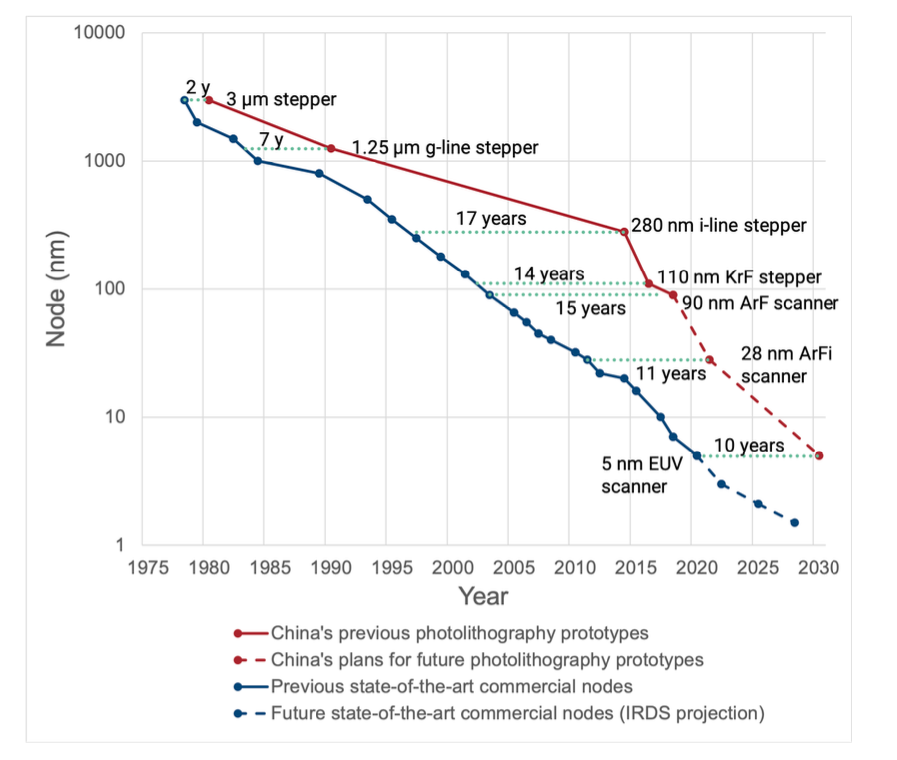
Lithography Equipment: ASML, a Dutch company, reigns supreme in advanced lithography technologies, with China facing restrictions on acquiring cutting-edge equipment. While Chinese counterparts like Shanghai Micro Electronics Equipment (SMEE) aspire to bridge the gap, their progress remains sluggish, hampering China’s efforts to catch up with the technology frontier.
Deposition and Etching Equipment: Chinese producers have made strides in certain segments, primarily in trailing-edge processes. However, challenges persist in critical and leading-edge applications, limiting their competitiveness on the global stage. The increased demand for deposition equipment in advanced manufacturing nodes further favors foreign incumbents, inhibiting the market penetration of Chinese equipment.
Process Control Equipment: This segment poses significant barriers to entry due to its critical nature and high technical complexity. Incumbents leverage their established customer base and data analytics capabilities to maintain dominance, while Chinese vendors struggle to make substantial headway beyond basic tasks.
China’s Response:
Here are some of the leading Semiconductor Equipment companies of China:
- Naura Technology Group: China’s largest chip production equipment manufacturer. They offer a comprehensive product portfolio including etching, deposition, cleaning, and annealing equipment. They are a supplier to major players like SMIC, Huawei, and Samsung .
- AMEC (Advanced Micro-Fabrication Equipment Inc.): Specializes in CVD systems, epitaxial deposition systems, and diffusion furnaces. They are known for their innovative solutions and proprietary technologies .
- Beijing Jingyi Century Automatic Equipment Co. Ltd (Jingyi): A manufacturer of etching, deposition, and cleaning equipment .
- Shanghai Micro Electronics Equipment Co. Ltd (SMEE): Manufactures wet process equipment, including cleaners, wet etchers, and electroplaters and lithography tools.
- BeiJing ZhongKeXin Electronics Equipment Co. Ltd (ZKX): Specializes in diffusion furnace, RTP furnace, and MOCVD equipment .
Read More: Chinese Lithography Giant SMEE to File IPO with 28nm Capability
It’s important to note that China’s semiconductor equipment industry is still developing, and these companies are smaller than their established foreign counterparts. However, with significant government support and ongoing research and development, they are making strides towards domestic production and reducing their reliance on foreign imports.
Image Credits: China’s Progress in Semiconductor Manufacturing Equipment
Read More: 5 High Growth Stocks From the World of Semiconductors – techovedas
Conclusion
In conclusion, the intricate interplay between technological advancement, market dynamics, and regulatory frameworks underscores the complexities inherent in the semiconductor industry’s global landscape. As stakeholders navigate these challenges, fostering innovation, collaboration, and strategic partnerships will be imperative in shaping the future of semiconductor manufacturing.



When the West, especially when United States of Amnesia is leading, they will talk about freetrade n international rules based order.
The moment they lost their competitiveness, all sorts of obstacles n barriers will be erected in the name of national security.
These sore loser n bullying behaviours has become clear for the rest of the world to see what a hypocrite these so called human rights West. They are nothing but a bunch of pale faced with forked tongues characters