Introduction
In the realm of storage devices, Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and Solid-State Drives (SSDs) stand out as the two primary options available to consumers. While both serve the purpose of storing data, they exhibit significant differences in terms of technology, performance, and reliability. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the seven key distinctions between HDDs and SSDs, providing a detailed comparison to help you understand which option best suits your needs.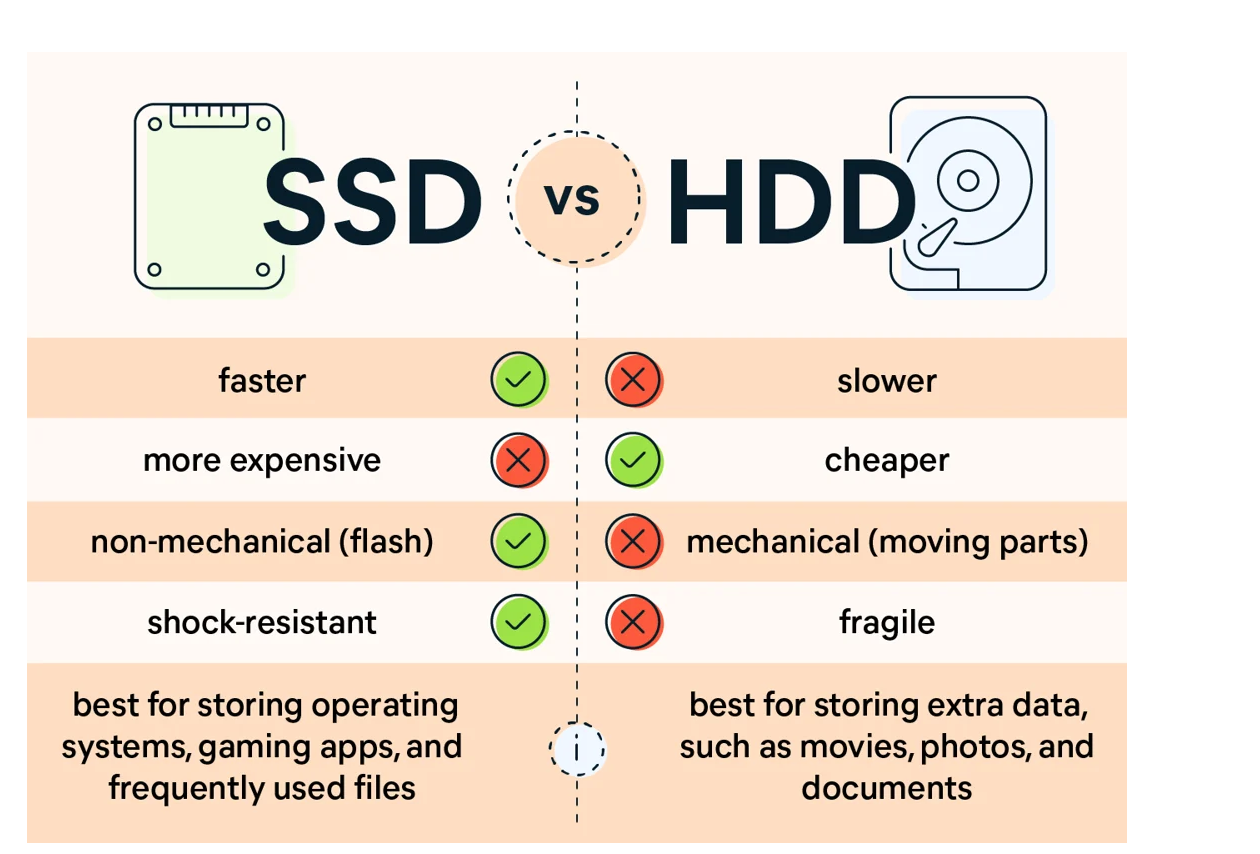
1. Technology and Construction
| Feature | HDD | SSD |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Medium | Magnetic spinning platters | Flash memory chips |
| Moving Parts | Spinning disks, mechanical arm | No moving parts |
| Wear and Tear | Susceptible to mechanical failure | Less prone to mechanical failure |
Explanation: HDDs store data on magnetic spinning platters, with a read/write head accessing data by moving across the platters. This mechanical process makes them vulnerable to wear and tear over time. Conversely, SSDs utilize flash memory chips to store data, eliminating the need for moving parts and reducing the risk of mechanical failure.
Read More: What is Microelectronics: Applications, Significance and Challenges – techovedas
2. Speed and Performance
| Feature | HDD | SSD |
|---|---|---|
| Access Time | Slower due to mechanical delays | Faster access times |
| Read/Write Speed | Limited by disk rotation speed | Consistently high read/write speeds |
Explanation: The access time of HDDs is slower due to the mechanical process of physically positioning the read/write head over the spinning disk. In contrast, SSDs offer faster access times as there are no moving parts involved. Additionally, SSDs provide consistently high read/write speeds, enhancing overall system performance.
Read More: Which Country has Highest No. of Semiconductor Fabs
3. Power Consumption and Noise
| Feature | HDD | SSD |
|---|---|---|
| Power Consumption | Higher power consumption due to moving parts | Lower power consumption |
| Noise | Audible noise during operation | Silent operation |
Explanation: HDDs consume more power during operation due to the movement of spinning disks and mechanical components. This higher power consumption contributes to increased heat generation and noise levels. In contrast, SSDs consume less power since they lack moving parts, resulting in silent operation and lower energy consumption.
4. Durability and Shock Resistance
| Feature | HDD | SSD |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Prone to mechanical failure | More durable and resistant to shocks |
| Shock Resistance | Susceptible to damage from physical shocks | Resistant to physical impacts |
Explanation: HDDs are susceptible to damage from physical shocks and vibrations due to their mechanical components. In contrast, SSDs are more durable and resistant to physical impacts since they have no moving parts. This makes SSDs ideal for use in portable devices where durability is crucial.
Read More: TSMC set to start constructing German fab in 2H24 : 5 Major Highlights – techovedas
5. Lifespan and Longevity
| Feature | HDD | SSD |
|---|---|---|
| Lifespan | Limited lifespan due to mechanical wear and tear | Longer lifespan with no moving parts |
| Wear Leveling | Not applicable | Extensive wear leveling algorithms |
Explanation: HDDs have a limited lifespan due to mechanical wear and tear resulting from the constant movement of internal components. SSDs, however, employ wear leveling algorithms to distribute write cycles evenly across memory cells, thereby extending their lifespan. This results in SSDs having a longer overall lifespan compared to HDDs.
Read More:7 Mind-Blowing Features of Gemini 1.5 : Google’s Answer to ChatGPT – techovedas
6. Temperature Sensitivity
| Feature | HDD | SSD |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Sensitivity | Sensitive to temperature fluctuations | Less sensitive to temperature changes |
Explanation: HDDs are sensitive to temperature fluctuations, which can affect their performance and reliability. Changes in temperature can lead to expansion or contraction of mechanical components, potentially impacting the drive’s functionality. In contrast, SSDs are less sensitive to temperature changes since they have no moving parts, making them more resilient in varying environmental conditions.
Read More: Explained: What is CMOS Technology? – techovedas
7. Price and Storage Capacity
| Feature | HDD | SSD |
|---|---|---|
| Price | Lower cost per gigabyte | Higher cost per gigabyte |
| Storage Capacity | Higher storage capacities at a lower cost | Lower storage capacities at a higher cost |
Explanation: HDDs offer larger storage capacities at a lower cost per gigabyte compared to SSDs. This makes HDDs a more economical choice for users requiring large amounts of storage space on a budget. However, SSDs are generally more expensive per gigabyte but provide faster performance and improved reliability, making them ideal for users prioritizing speed and efficiency over storage capacity.
Follow us on Linkedin for everything around Semiconductors & AI
Conclusion
In conclusion, HDDs and SSDs exhibit several distinct differences in terms of technology, performance, durability, and price. While HDDs offer larger storage capacities at a lower cost, they are prone to mechanical failure and slower performance. On the other hand, SSDs provide faster access times, improved reliability, and better durability, albeit at a higher cost. When choosing between HDDs and SSDs, consider your specific requirements, budget, and performance needs to make an informed decision.



